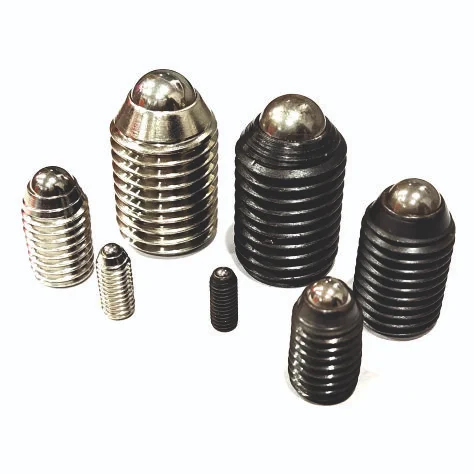
Plungers – Precision Components for Mechanical and Industrial Applications
Vivek Kumar / Date: 08 Oct, 2025
Plungers are essential components used in a wide range of mechanical and industrial applications. They provide accurate positioning, secure locking, and smooth movement in assemblies, control panels, machinery, and equipment. From spring plungers that enable repeatable positioning to indexing plungers for locking mechanisms, each type serves a specific purpose in improving operational efficiency.
This article explores the different types of plungers, their applications, construction features, and advantages, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these components contribute to mechanical systems.
Understanding Plungers
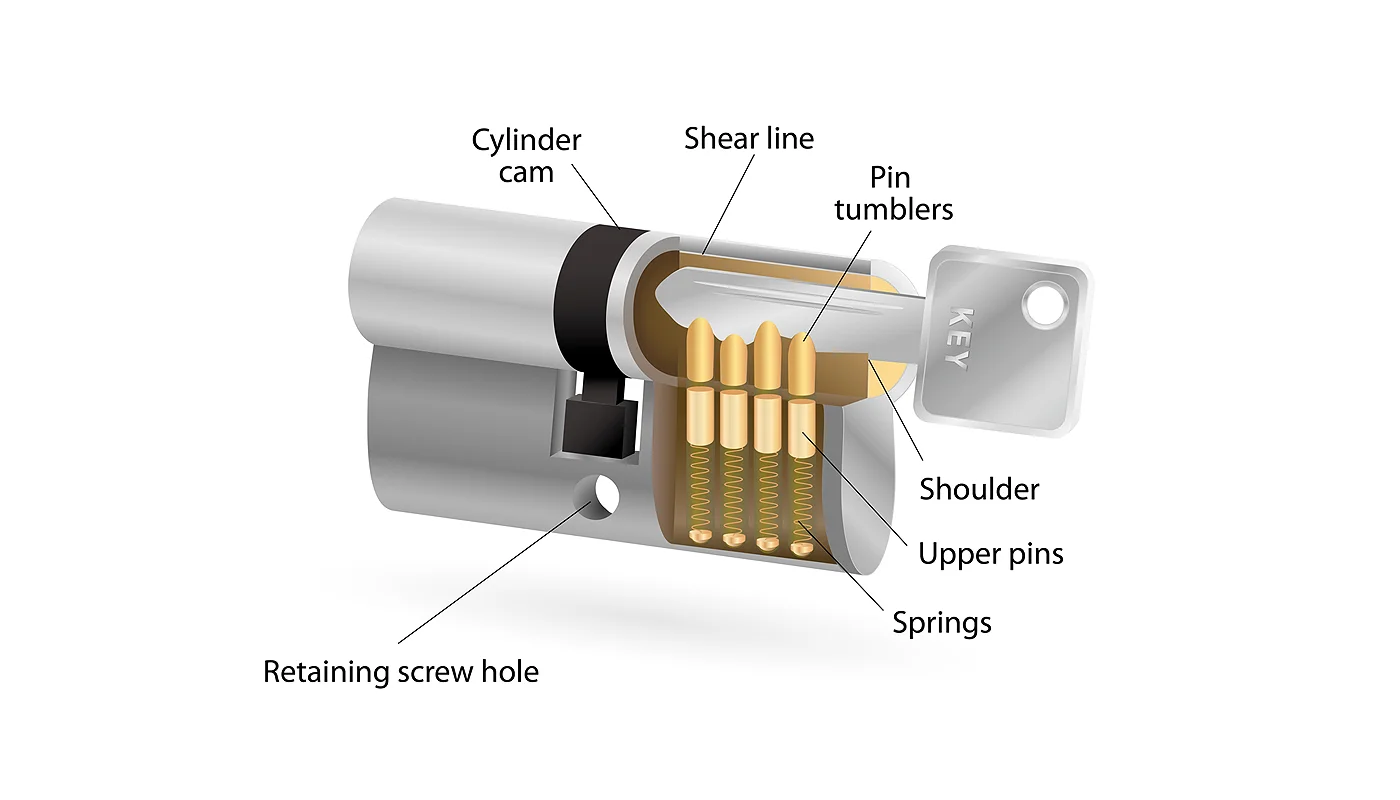
A plunger is a mechanical device that typically consists of a shaft or pin that moves within a housing, often spring-loaded, to engage or disengage with another component. Plungers are widely used for positioning, locking, indexing, and detent applications.
The main types of plungers include:
-
Spring plungers
-
Ball plungers
-
Indexing plungers
-
Plunger pins
Each type has unique features and applications, which will be discussed in detail.
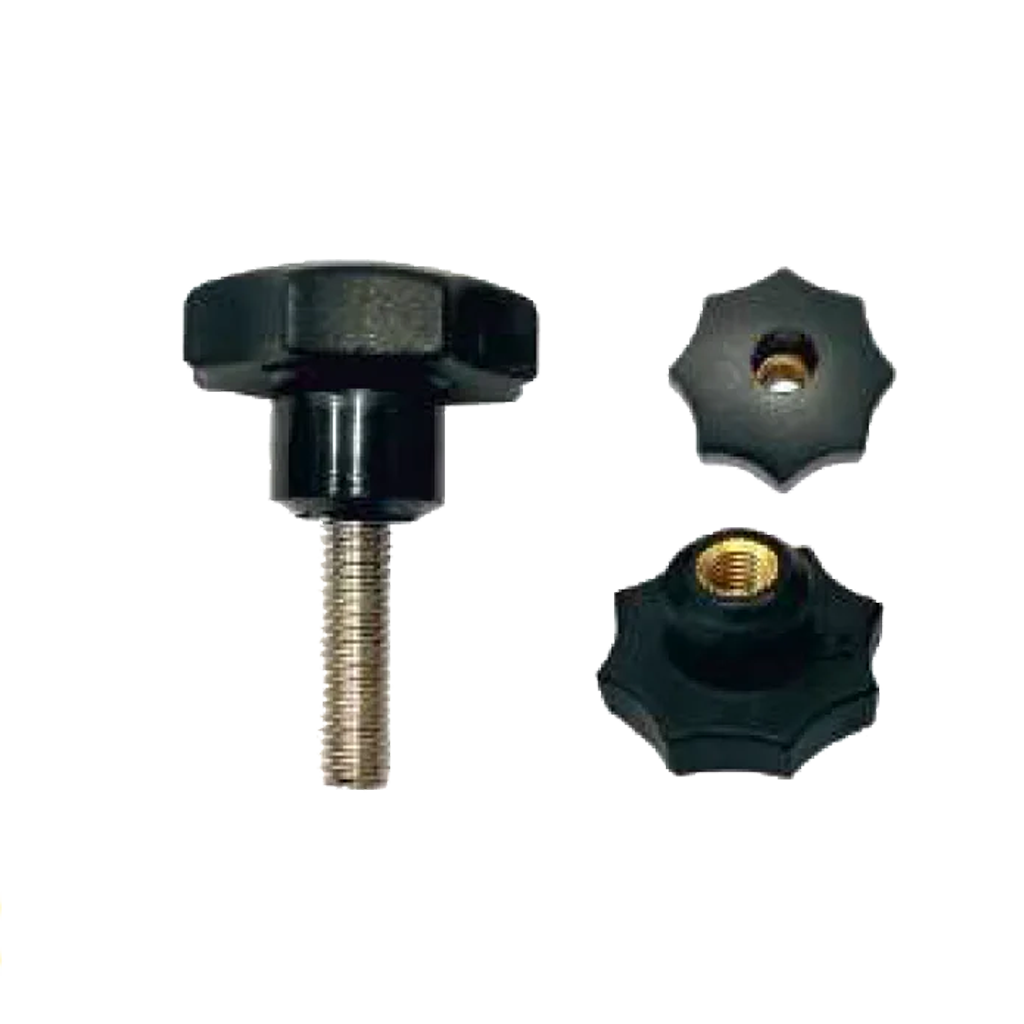
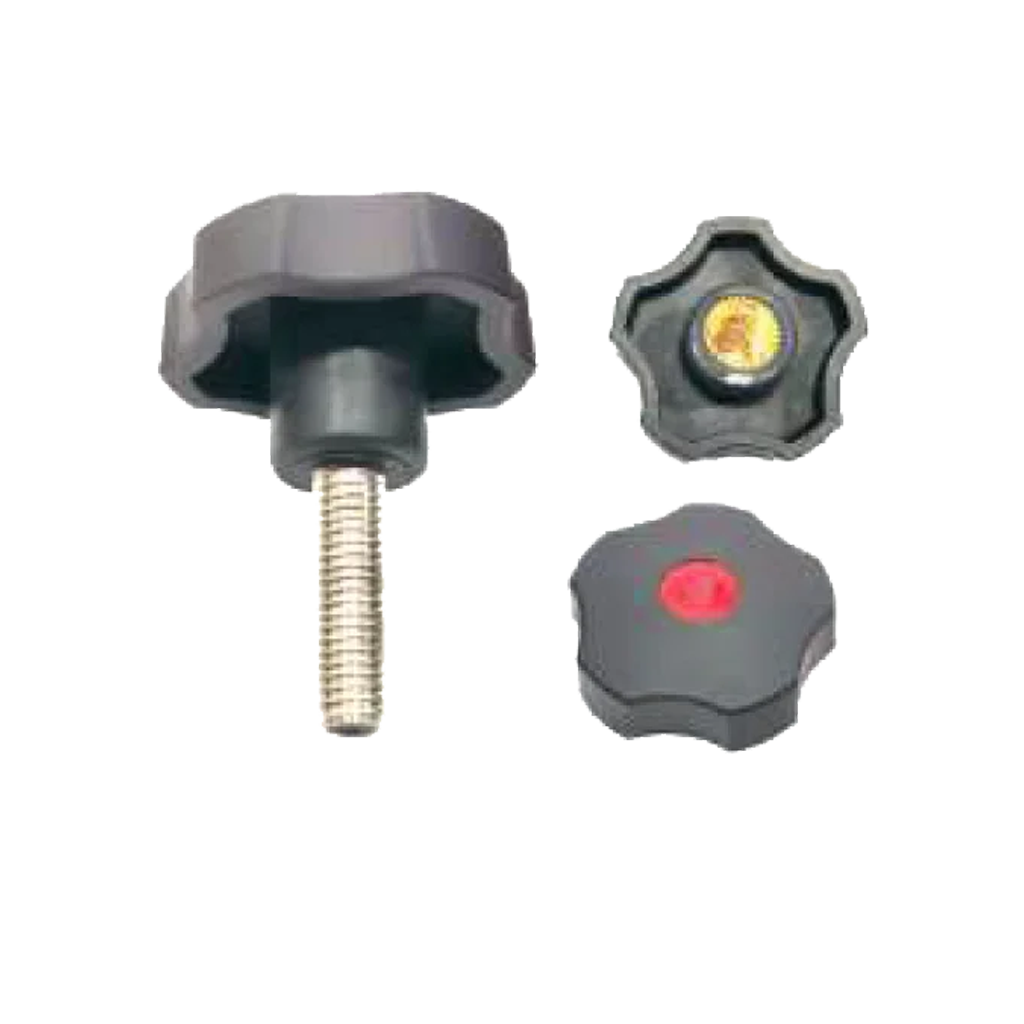
Spring Plungers – Controlled Positioning
Spring plungers are designed to apply consistent force to a component, ensuring reliable positioning in assemblies and mechanical setups. They are commonly used in jigs, fixtures, control panels, and industrial machinery where repeatable alignment is required.
Features of Spring Plungers
-
Spring-loaded mechanism for consistent tension
-
Threaded or unthreaded designs for different mounting options
-
Hardened pins or shafts for accurate engagement
-
Corrosion-resistant coatings to withstand environmental exposure
Applications of Spring Plungers
-
Repositioning components in assembly lines
-
Engaging detents in control mechanisms
-
Securing movable parts in equipment
-
Acting as mechanical stops in machinery
Spring plungers allow components to move smoothly into place, reducing operational errors and improving efficiency in mechanical systems.
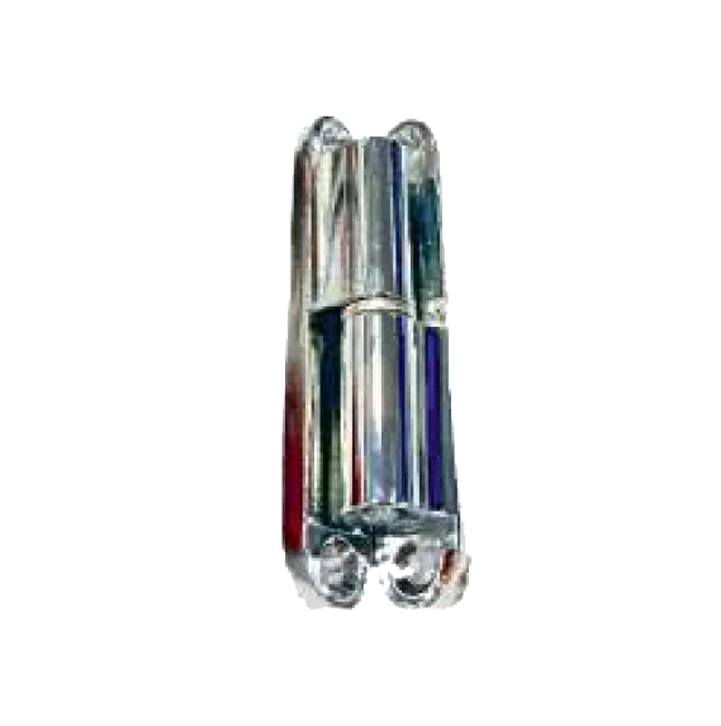
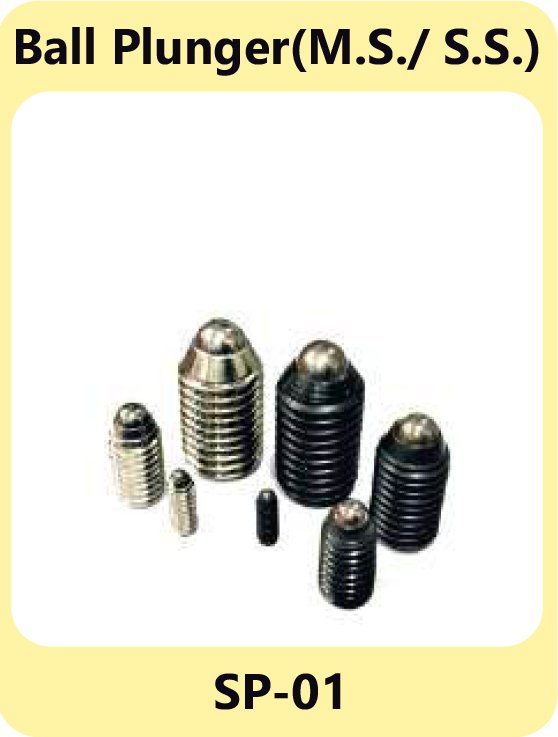
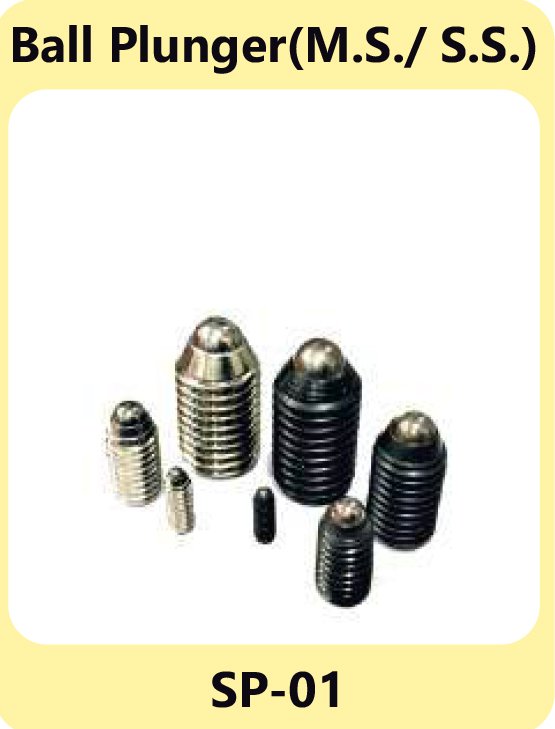
Ball Plungers – Smooth Engagement
Ball plungers use a spring-loaded ball to achieve smooth engagement and disengagement. They are ideal for applications that require indexing, detents, or precise positioning in tight spaces.
Key Characteristics
-
Spring-loaded ball for flexible engagement
-
Stainless steel or alloy construction for resistance to wear
-
Compact design suitable for confined assemblies
-
Adjustable tension in some models for precise operation
Common Uses
-
Indexing positions in mechanical assemblies
-
Holding components in jigs or fixtures
-
Acting as detents in control panels or mechanical stops
-
Providing smooth motion in automation equipment
Ball plungers reduce friction and allow components to move with minimal effort while maintaining accurate positioning.
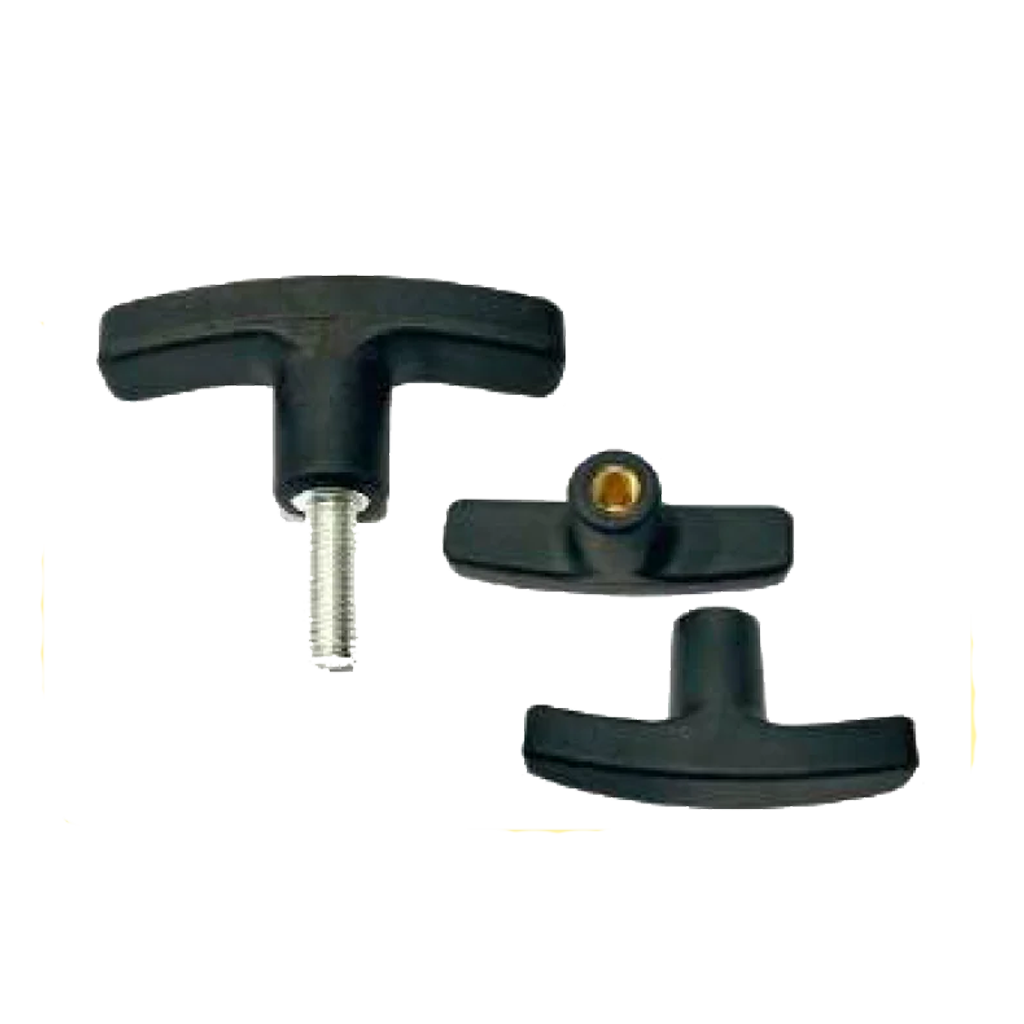
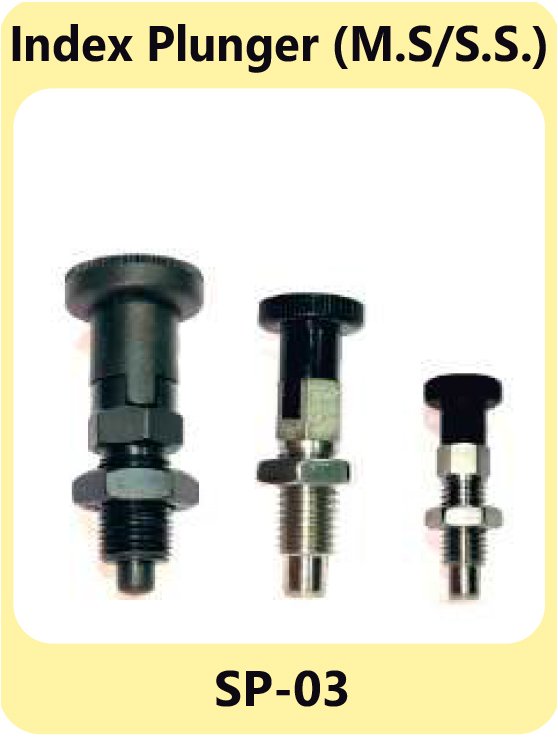
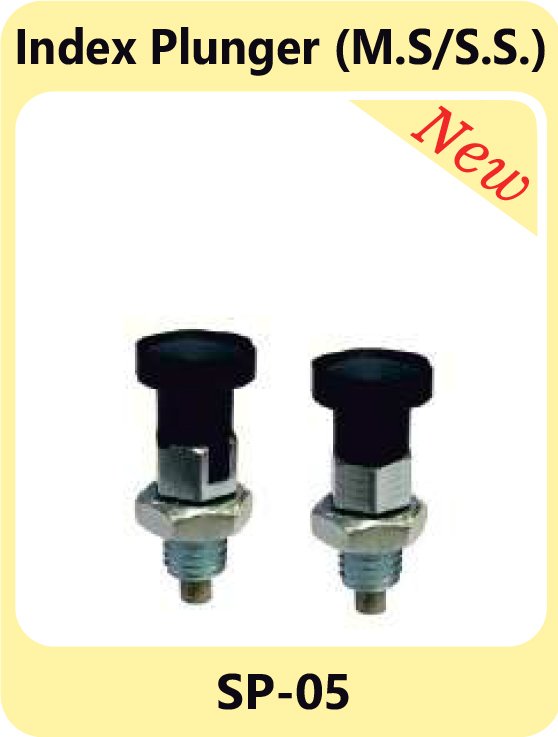
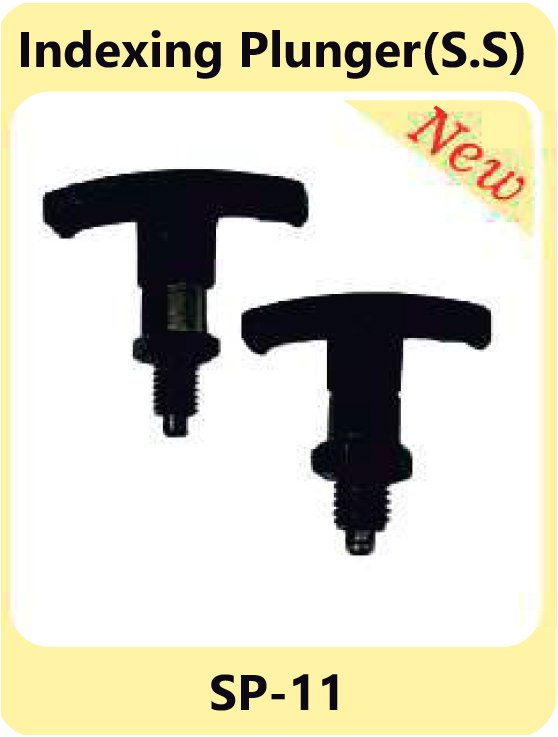
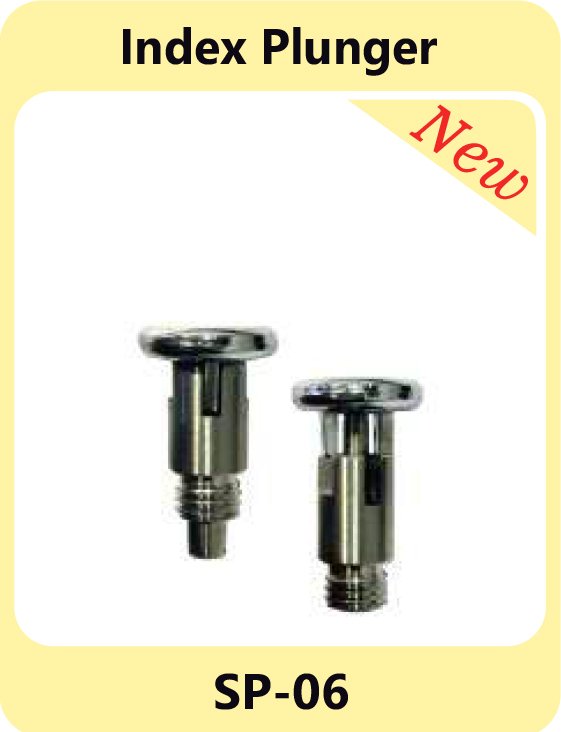
Indexing Plungers – Secure Locking Mechanisms
Indexing plungers are used to lock movable parts in place. They are widely used in equipment that requires frequent adjustments or precise positioning. These plungers ensure stability and reliability in assemblies where fixed positions are critical.
Features of Indexing Plungers
-
Locking pin for secure engagement
-
Easy-to-operate handle or knob for repositioning
-
Threaded body for simple installation
-
Corrosion-resistant or heat-treated materials for extended use
Applications
-
Adjustable machine parts and equipment
-
Rotating assemblies that require indexing positions
-
Control panels with movable components
-
Fixtures where repeated locking and unlocking are necessary
Indexing plungers simplify operations by enabling secure, repeatable positioning, reducing the risk of misalignment or movement during use.
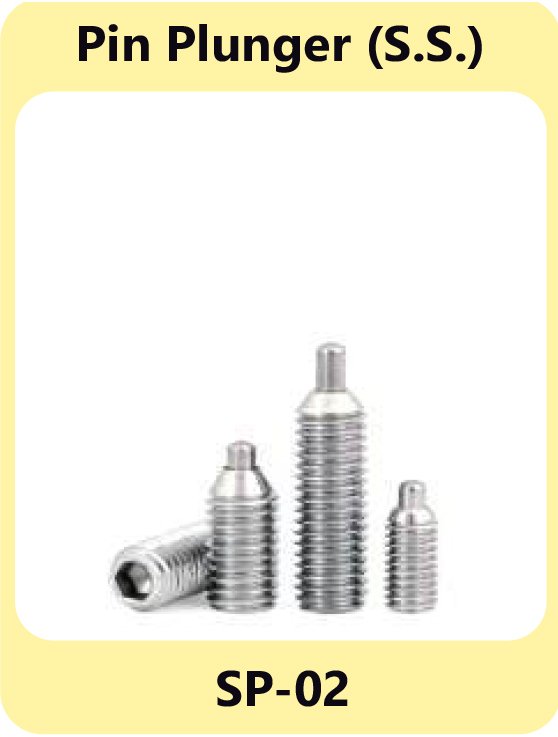
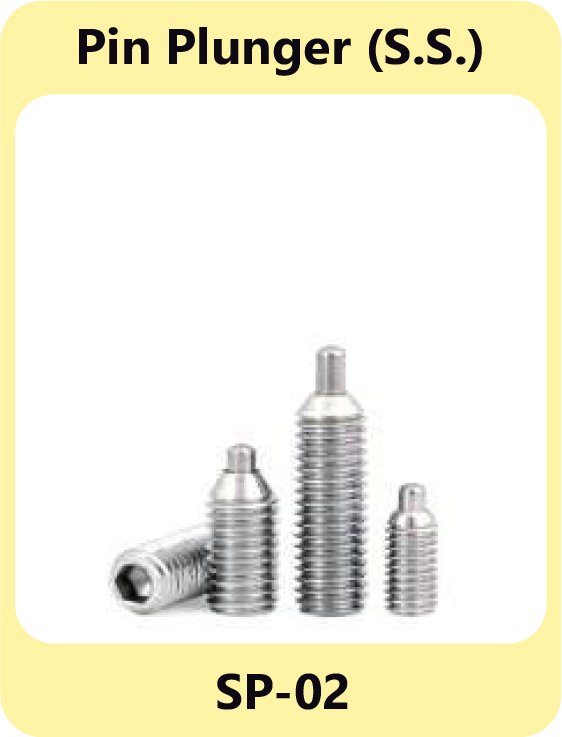
Plunger Pins – Accurate Alignment and Holding
Plunger pins are solid components used to hold, align, or position mechanical parts in assemblies. Unlike spring or ball plungers, they do not have a spring mechanism but are designed to provide precise engagement in control panels or machinery.
Features of Plunger Pins
-
Straight pins or tapered designs for alignment
-
Stainless steel or treated alloys for wear resistance
-
Tight tolerances for precise positioning
-
Smooth finish for low friction in mechanical operations
Applications
-
Pinning components in control panel assemblies
-
Aligning mechanical parts in fixtures or jigs
-
Acting as positioning stops in machinery
-
Providing reference points in repetitive operations
Plunger pins play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and stability of mechanical assemblies, reducing errors, and enhancing operational performance.
Construction and Material Considerations
The performance of a plunger depends heavily on its construction and the materials used. Common considerations include:
-
Material: Stainless steel, alloy steel, and treated metals are widely used to resist wear and environmental exposure.
-
Coating: Corrosion-resistant coatings protect plungers in humid or chemically active environments.
-
Tolerance: Precision machining ensures tight tolerances for consistent engagement and minimal play.
-
Spring Quality: In spring-loaded plungers, high-quality springs maintain tension over extended use.
Choosing the right material and construction method improves reliability, reduces maintenance, and ensures smooth operation in demanding applications.
Advantages of Using Plungers
Plungers offer several operational benefits:
-
Consistent and repeatable positioning in assemblies
-
Smooth engagement and disengagement with minimal friction
-
Secure locking and indexing for adjustable components
-
Low maintenance requirements due to high-quality materials
-
Reduced operational errors and downtime in mechanical systems
By selecting the appropriate type of plunger, industries can enhance efficiency, simplify machine setups, and ensure precise performance across multiple applications.
Applications Across Industries
Plungers are used in a wide range of industries, including:
-
Manufacturing: For positioning and locking components in assembly lines and machinery.
-
Automation: In robotics and automated equipment for smooth movement and indexing.
-
Control Panels: For securing and aligning electrical or mechanical components.
-
Marine and Outdoor Equipment: Corrosion-resistant plungers perform reliably in harsh environments.
-
Industrial Machinery: For repeatable positioning and locking in adjustable machinery parts.
The versatility of plungers makes them suitable for nearly any application that requires accurate movement, alignment, or locking.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Although plungers are low-maintenance, following these practices ensures consistent performance:
-
Regular cleaning to remove dust, debris, or chemical residues
-
Periodic inspection of spring tension in spring or ball plungers
-
Lubrication of moving parts where necessary
-
Checking alignment and engagement of indexing plungers and plunger pins
Proper maintenance minimizes wear, prevents operational errors, and extends the service life of plungers in mechanical systems.
Choosing the Right Plunger
Selecting the appropriate plunger depends on the application:
-
Use spring plungers for repeatable positioning or detent applications
-
Choose ball plungers for smooth engagement in tight assemblies
-
Opt for indexing plungers where secure locking and repeatable adjustment are needed
-
Select plunger pins for accurate alignment and holding in mechanical or control panel assemblies
Understanding the application requirements, operating environment, and load conditions ensures optimal plunger performance.
Conclusion
Plungers, including spring plungers, ball plungers, indexing plungers, and plunger pins, are integral to mechanical systems, industrial equipment, and control panels. They provide precise positioning, smooth operation, and secure locking, helping reduce errors, improve efficiency, and maintain operational consistency.
With proper selection, material choice, and maintenance, plungers ensure reliable performance across a wide range of applications, from manufacturing and automation to control systems and industrial machinery. Their versatility and engineering precision make them indispensable components in modern mechanical and industrial setups.
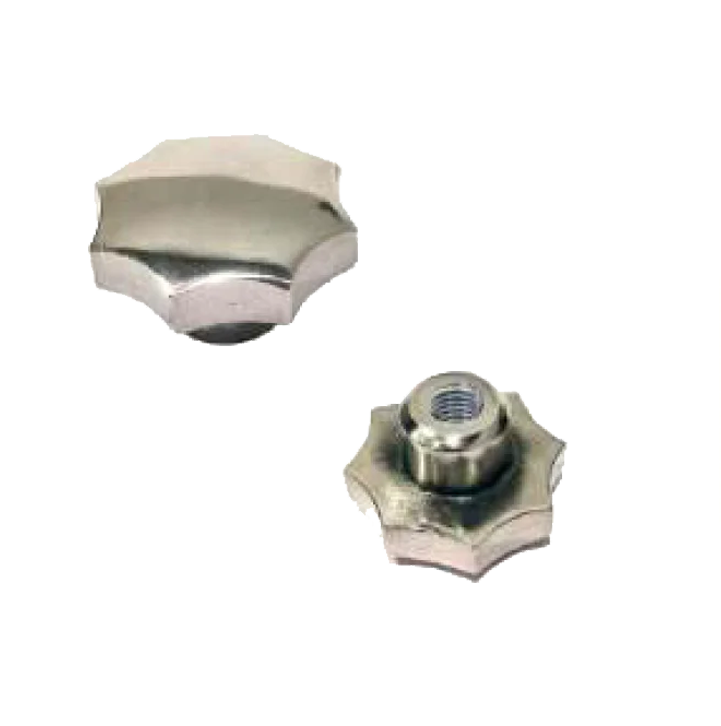
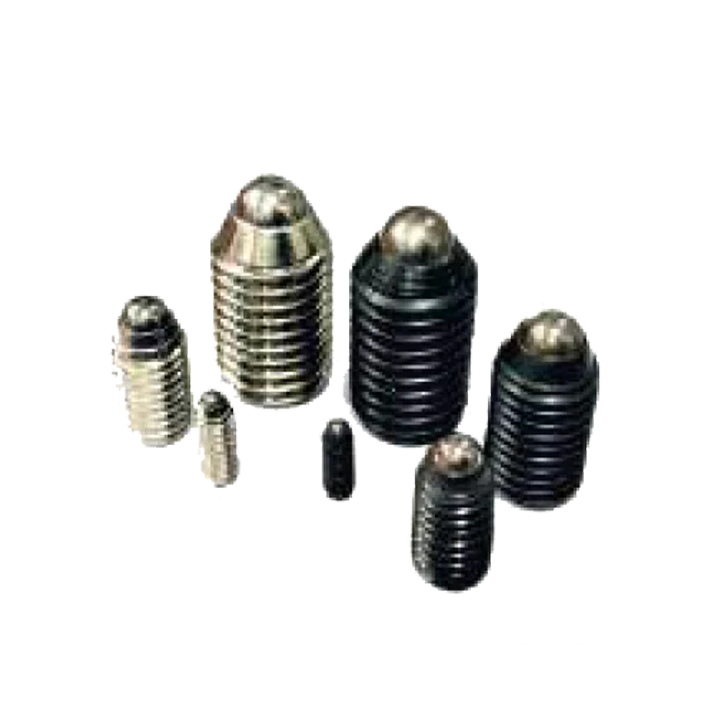 Ball Plunger M.S.& S.S. SP-01
Ball Plunger M.S.& S.S. SP-01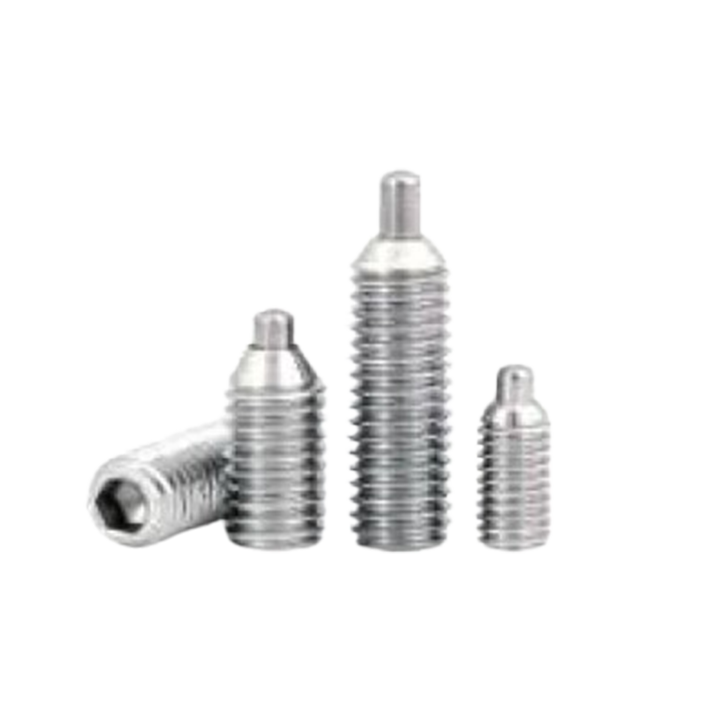 Pin Plunger S.S. SP-02
Pin Plunger S.S. SP-02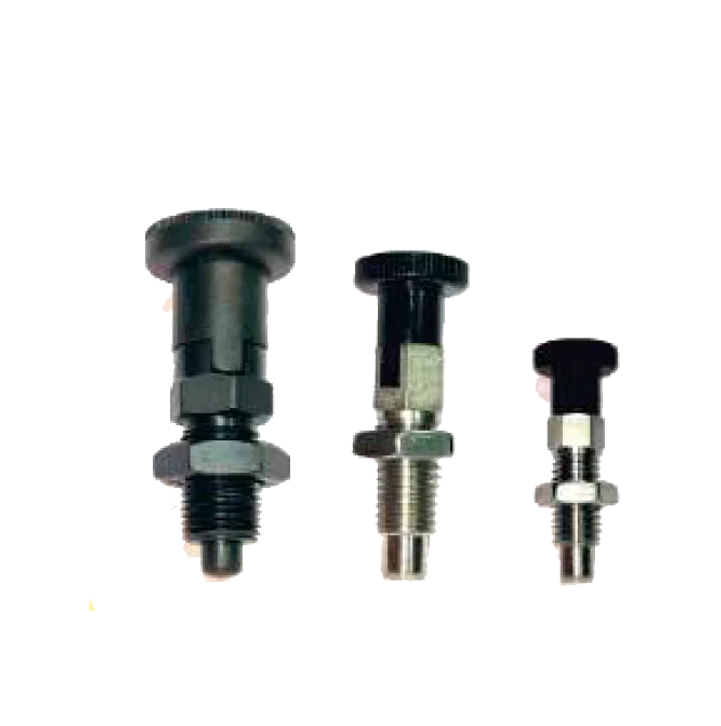 Index Plunger M.S& S.S. SP-03
Index Plunger M.S& S.S. SP-03 Index Plunger M.S& S.S. SP-05
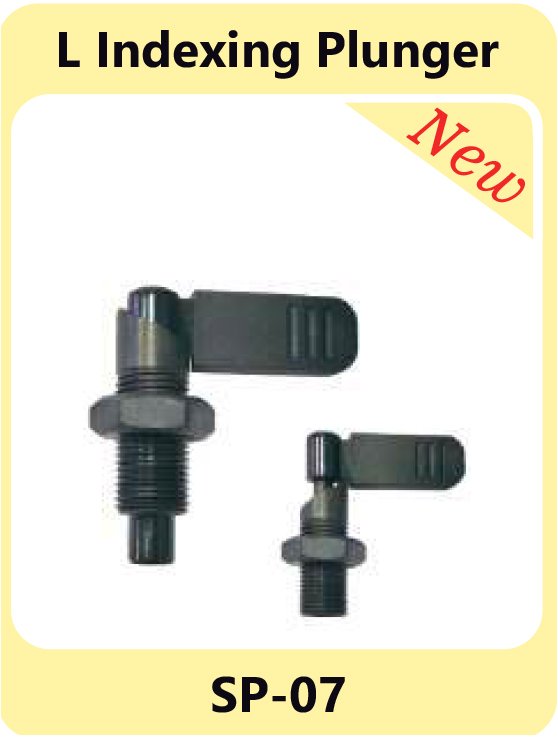
Index Plunger M.S& S.S. SP-05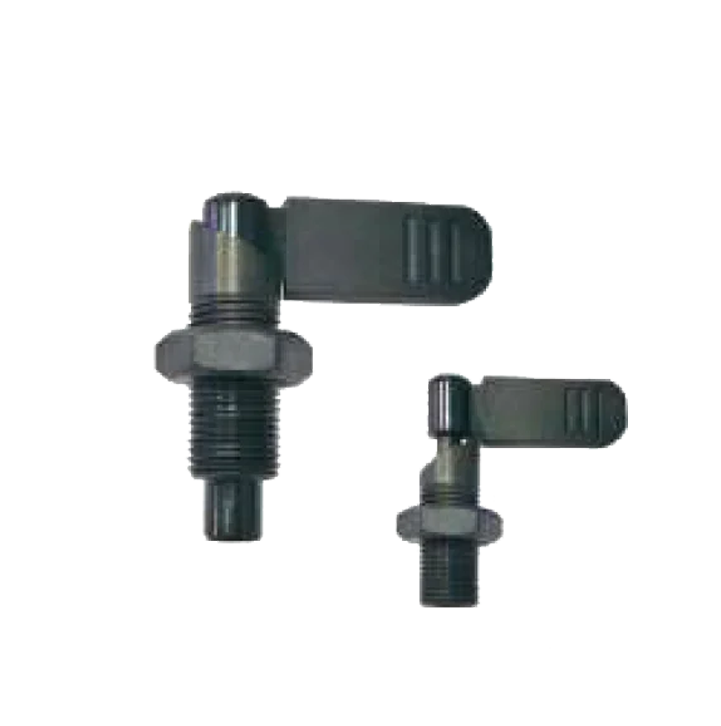 L Indexing Plunger SP-07
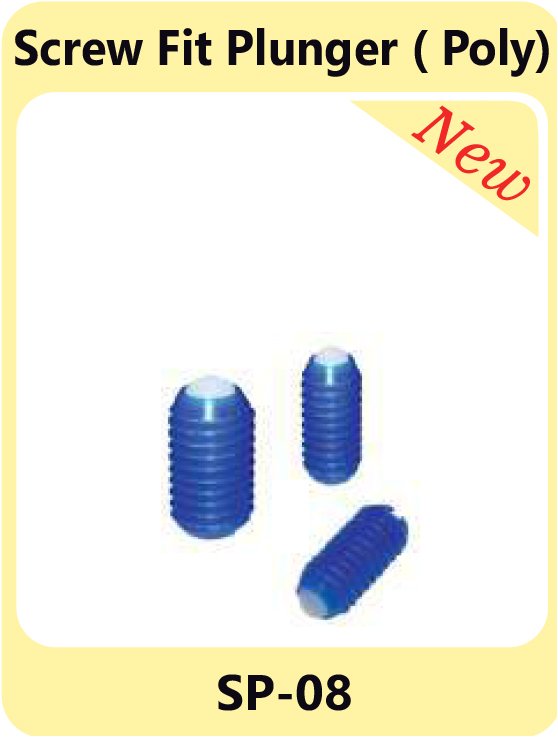
L Indexing Plunger SP-07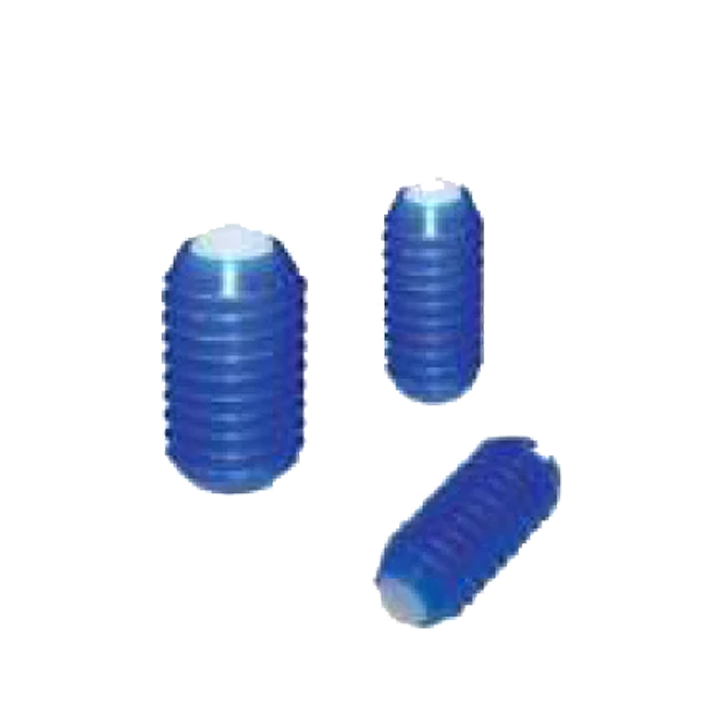 Screw Fit Plunger SP-08
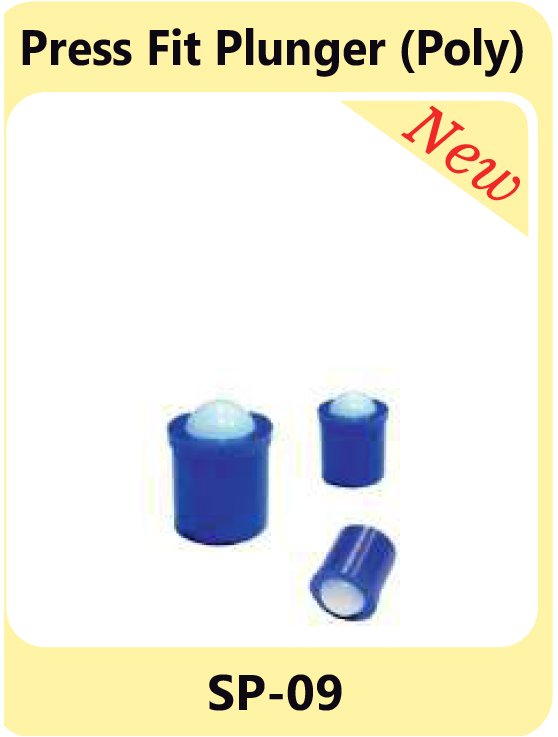
Screw Fit Plunger SP-08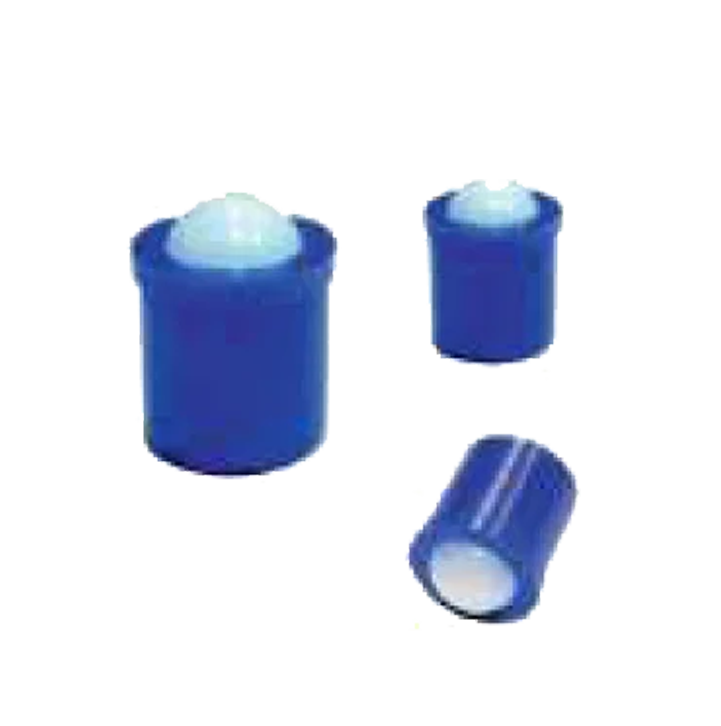 Press Fit Plunger SP-09
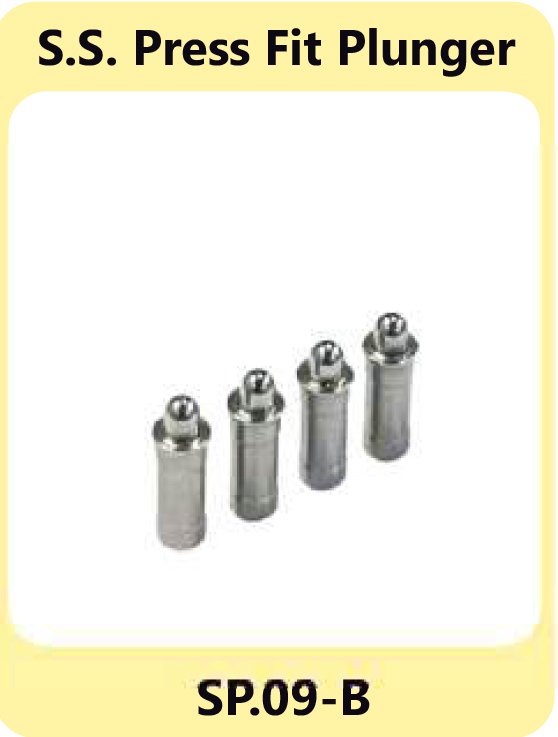
Press Fit Plunger SP-09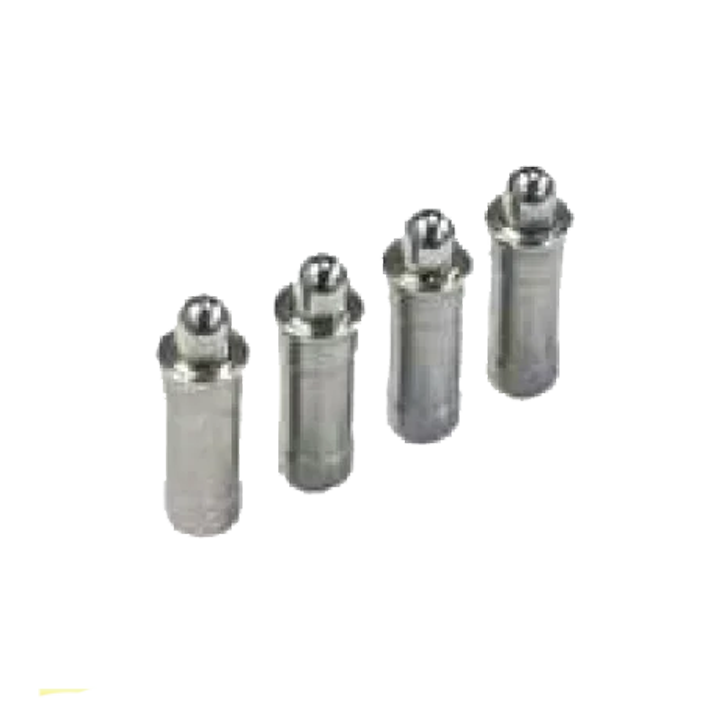 S.S. Press Fit Plunger SP.09-B
S.S. Press Fit Plunger SP.09-B Indexing Plunger SP-11
Indexing Plunger SP-11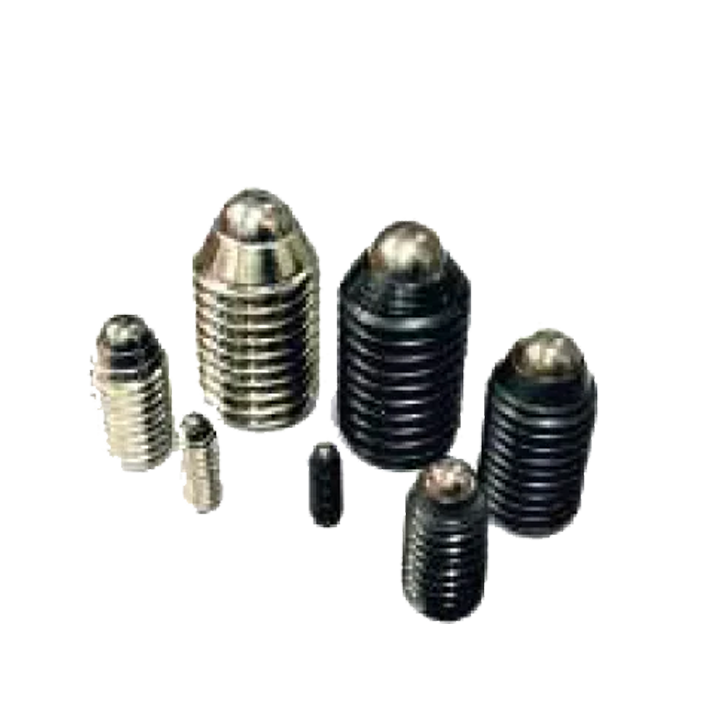 Ball Spring Plungers SP-01
Ball Spring Plungers SP-01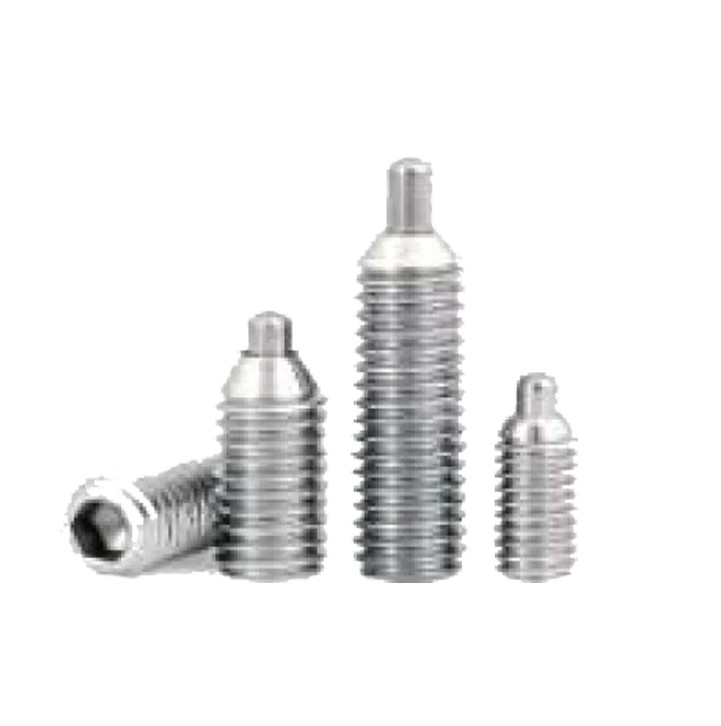 Pin Plungers SP-02
Pin Plungers SP-02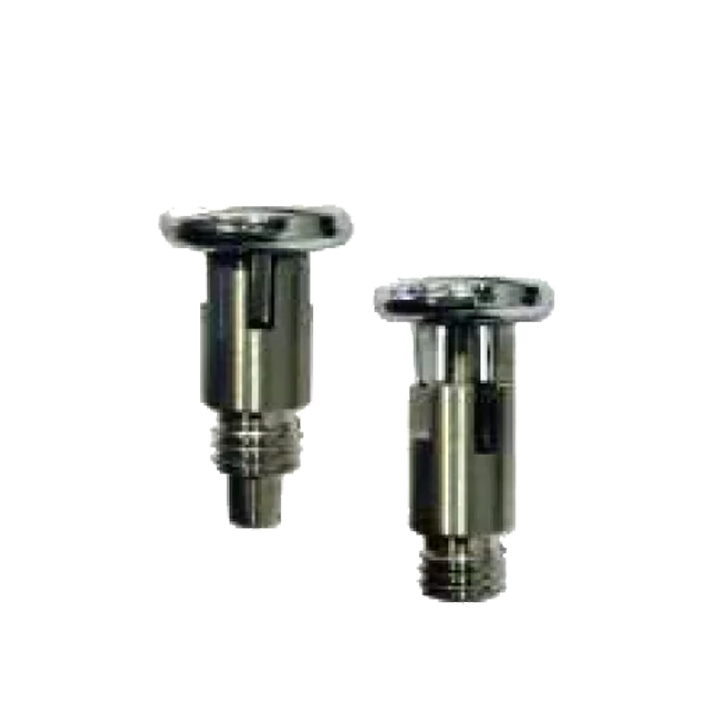 Index Plungers SP-06
Index Plungers SP-06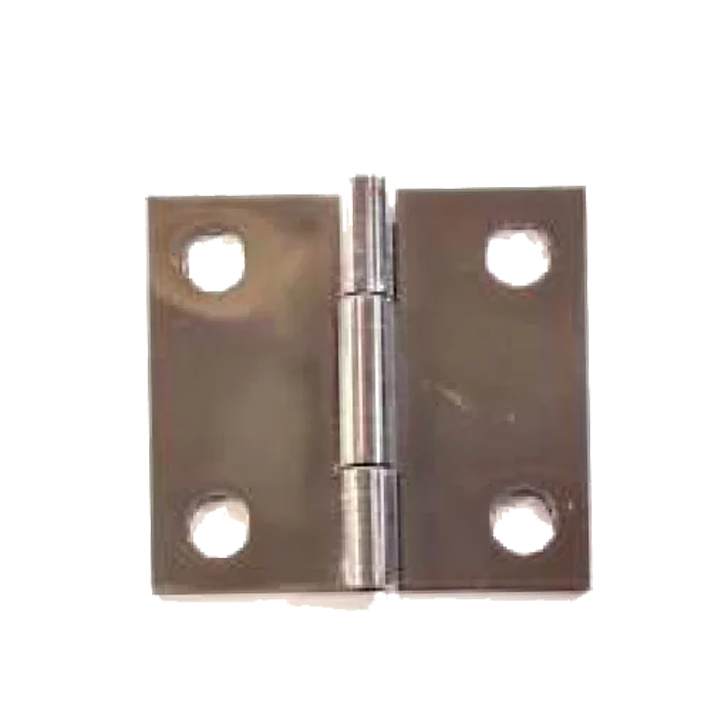 M.S.& S.S. Hinges HS-42
M.S.& S.S. Hinges HS-42 M.S.& S.S Concealed HS-43
M.S.& S.S Concealed HS-43 S.S.304 Piano Hinges HS-44
S.S.304 Piano Hinges HS-44 Metal Hinges HS-45
Metal Hinges HS-45 M.S. Hinges HS-52
M.S. Hinges HS-52 S.S. 5036 HS-53
S.S. 5036 HS-53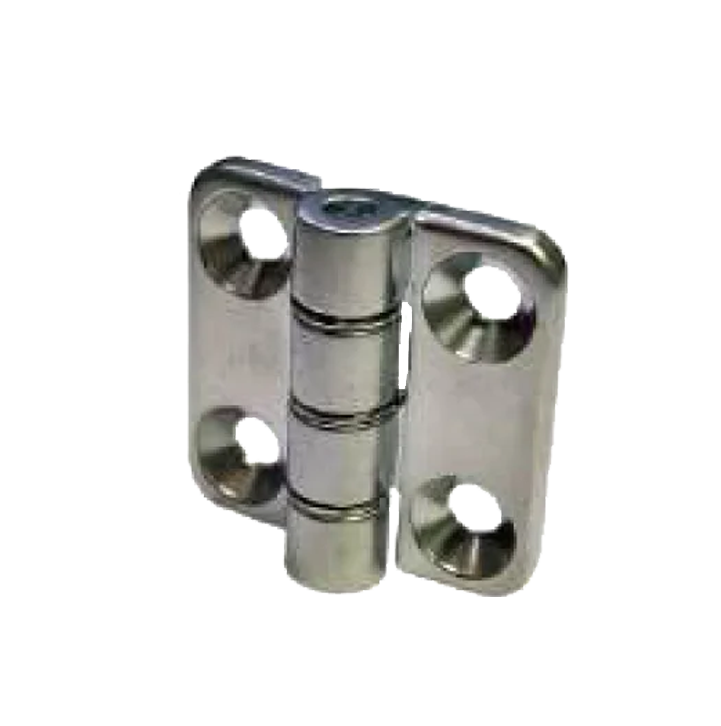 S.S. Hinges HS-54 N
S.S. Hinges HS-54 N Poly 98*70 HS-57 N
Poly 98*70 HS-57 N Die-Cast 60*49 HS-68 N
Die-Cast 60*49 HS-68 N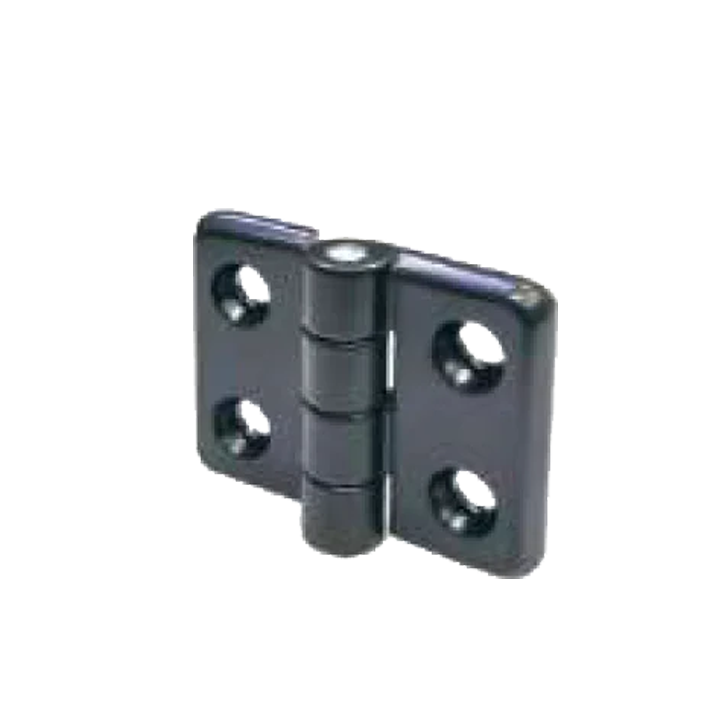 Die-Cast 50*40 HS-69 N
Die-Cast 50*40 HS-69 N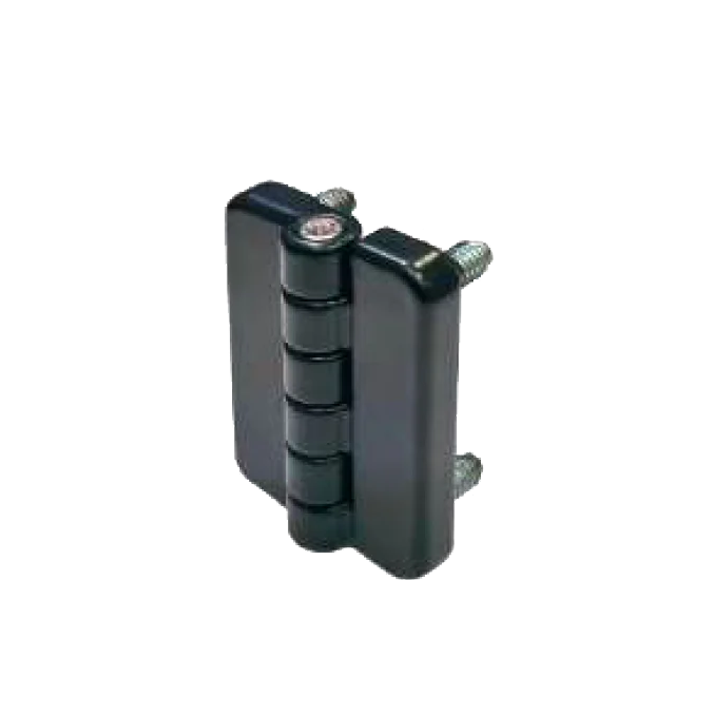 Die-Cast 54*40 Bolted HS-70 N
Die-Cast 54*40 Bolted HS-70 N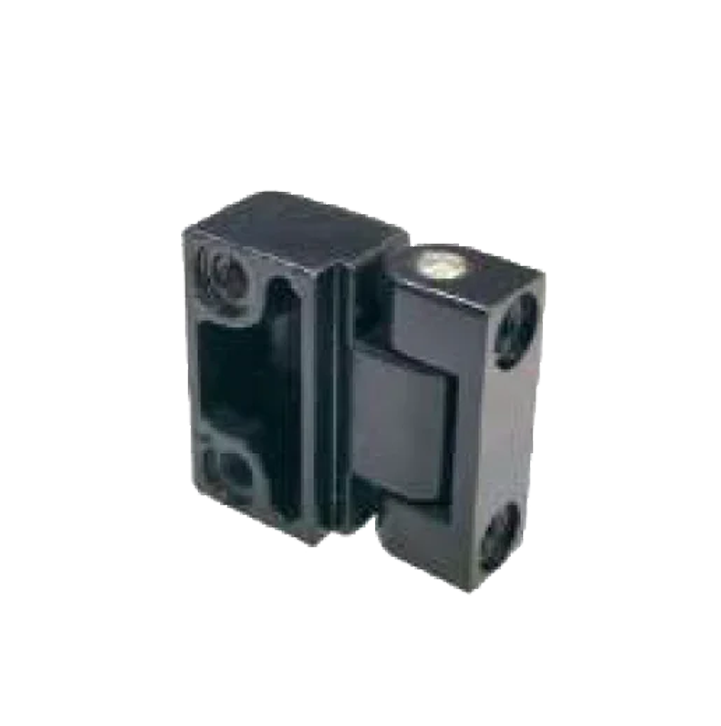 Damper Hinge 30mm HS-71 N
Damper Hinge 30mm HS-71 N Damper Hinge 50mm HS-72 N
Damper Hinge 50mm HS-72 N Bent Right Angle Hinge HS-73 N
Bent Right Angle Hinge HS-73 N DC Positioning Hinge HS-74 N
DC Positioning Hinge HS-74 N Brass 65*50 HS-75 N
Brass 65*50 HS-75 N Poly 92 HL-01
Poly 92 HL-01 Poly 120 HL-02
Poly 120 HL-02 Pocket Handle HL-05
Pocket Handle HL-05 Pocket Handle HL-05-B
Pocket Handle HL-05-B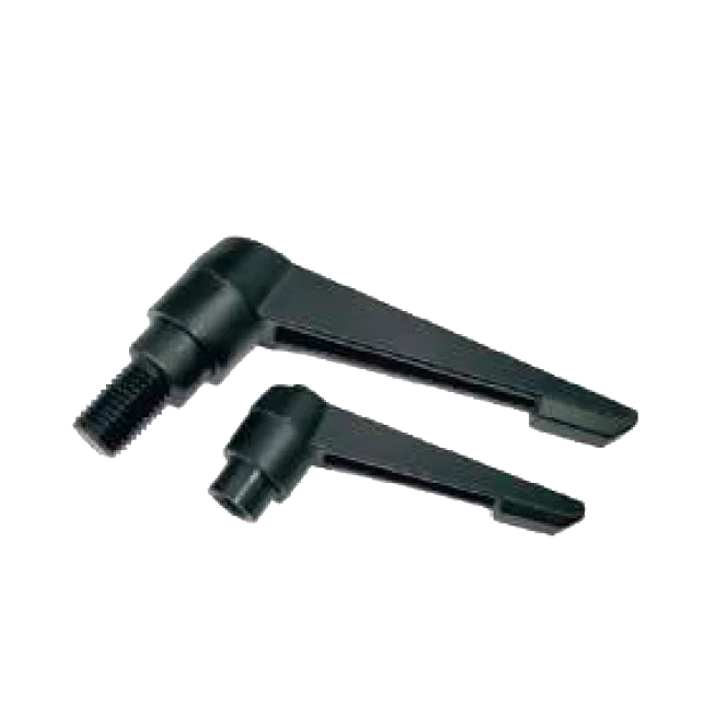 Die-Cast Adjustable HL-08
Die-Cast Adjustable HL-08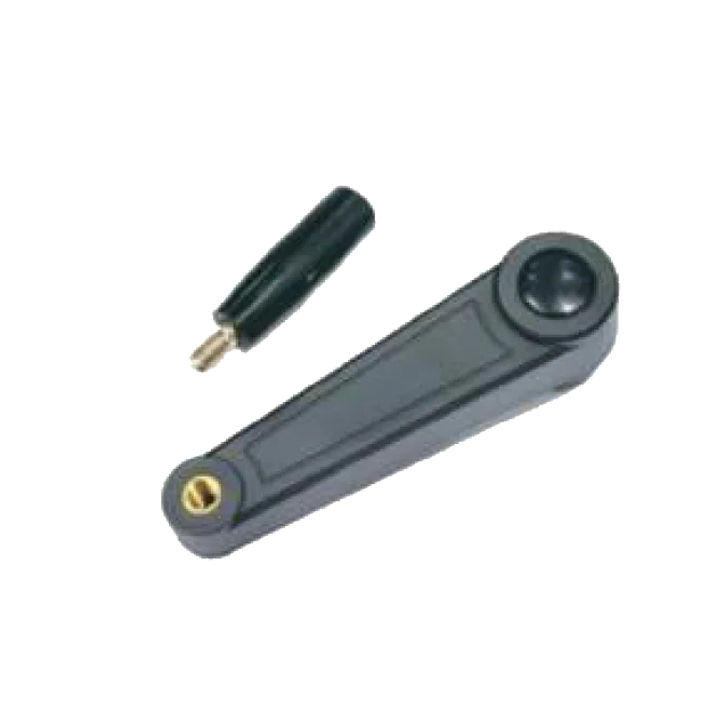 Polyamide Crank HL-11-A
Polyamide Crank HL-11-A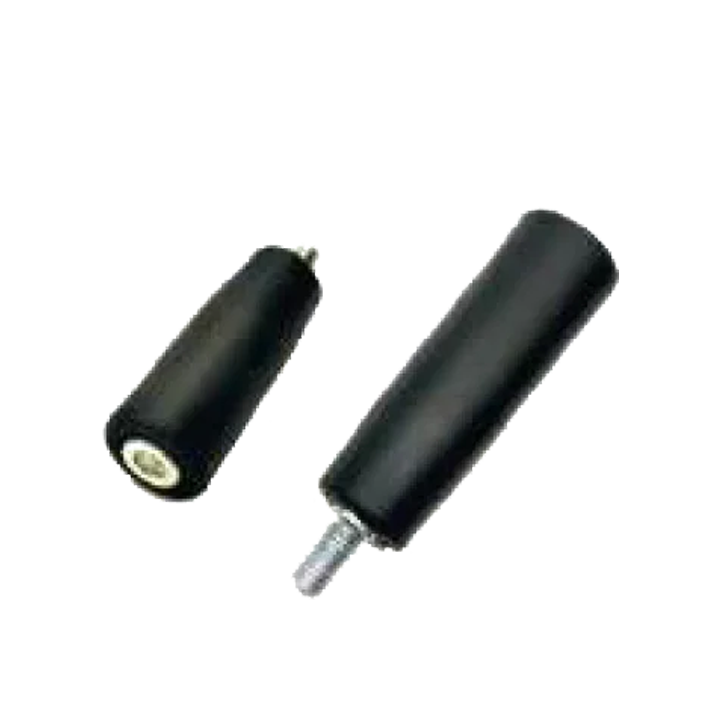 Poly Revolving Handle HL-12-A
Poly Revolving Handle HL-12-A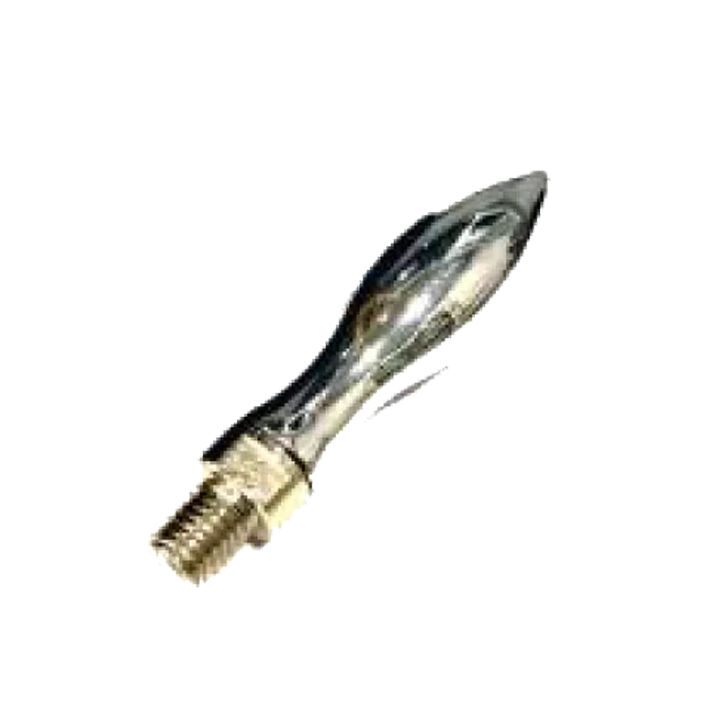 Curved Revolving Handle
Curved Revolving Handle M.S. Revolving Handle HL-12-C
M.S. Revolving Handle HL-12-C Metal Revolving Handle HL-12-E
Metal Revolving Handle HL-12-E Pipe Handle HL-13-B
Pipe Handle HL-13-B Pipe Handle HL-14
Pipe Handle HL-14 Poly HL-15
Poly HL-15 Poly HL-16
Poly HL-16 U-Handle Folding HL-17
U-Handle Folding HL-17 U-Handle Folding HL-19
U-Handle Folding HL-19 M.S. Handle HL-25
M.S. Handle HL-25 Poly Handle HL-20
Poly Handle HL-20 Strap Handle HL-21
Strap Handle HL-21 Pipe Handle HL-22
Pipe Handle HL-22 Pipe Handle HL-23
Pipe Handle HL-23 A.B.S. Handle HL-24
A.B.S. Handle HL-24 Poly HL-03
Poly HL-03 Polyamide Adjustable HL-09
Polyamide Adjustable HL-09 Polyamide Crank HL-11-B
Polyamide Crank HL-11-B Revolving Handle HL-12-D
Revolving Handle HL-12-D Pipe Handle HL-13-A
Pipe Handle HL-13-A Little Bracket 150mm CR-101
Little Bracket 150mm CR-101 Little Bracket 165mm CR-102
Little Bracket 165mm CR-102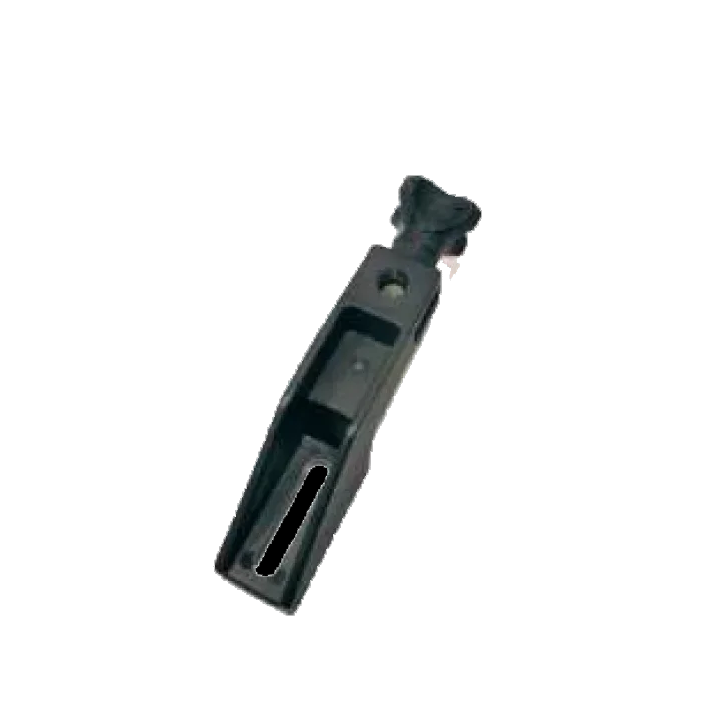 Little Bracket 195mm CR-103
Little Bracket 195mm CR-103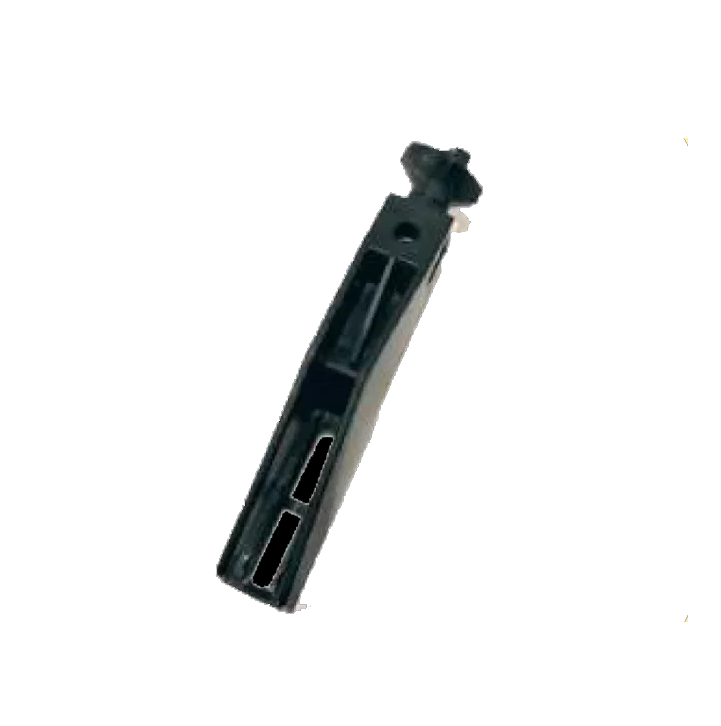 Side Bracket 245mm CR-104
Side Bracket 245mm CR-104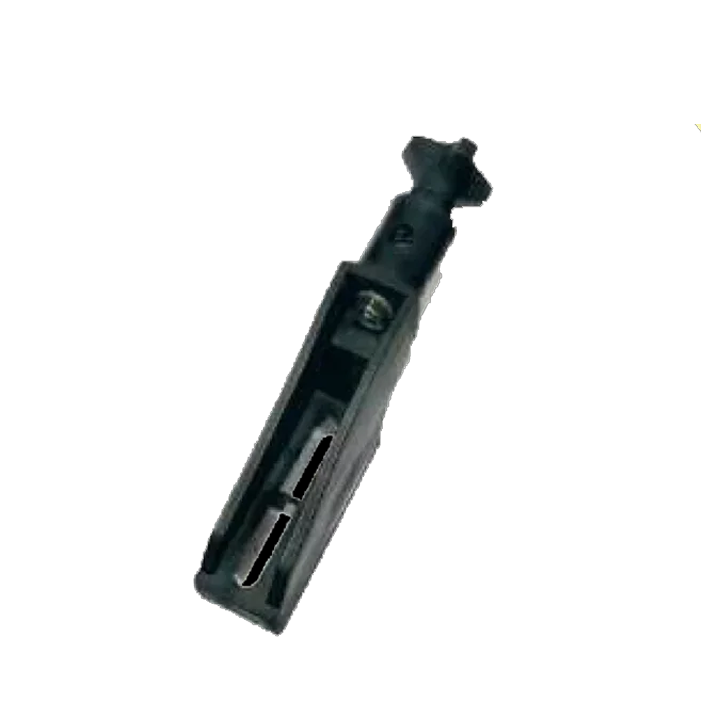 Swivel Bracket 245mm CR-105
Swivel Bracket 245mm CR-105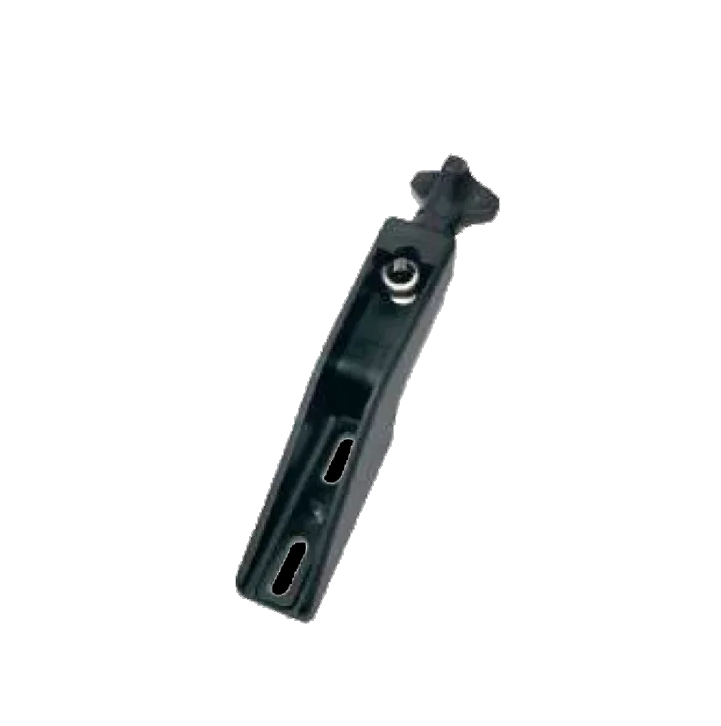 Side Bracket 228mm CR-106
Side Bracket 228mm CR-106 Single Clamp CR-109
Single Clamp CR-109 Double Clamp 40mm CR-112
Double Clamp 40mm CR-112 Double Clamp 68mm CR-113
Double Clamp 68mm CR-113 Single Clamp M6 CR-114
Single Clamp M6 CR-114 Single Rod Guide CR-121
Single Rod Guide CR-121 Drip Tray Holder CR-122
Drip Tray Holder CR-122 Metal Leveling Pad MLP-05
Metal Leveling Pad MLP-05 Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-01
Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-01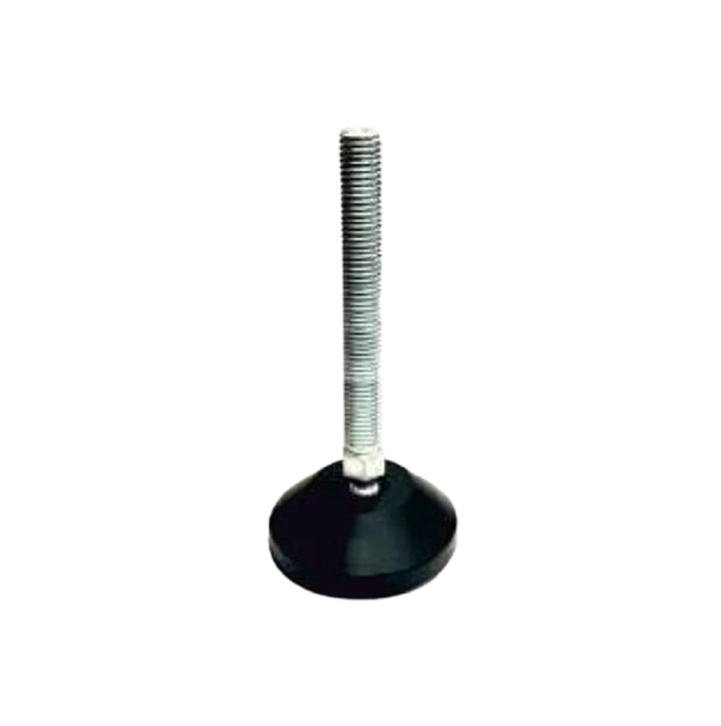 Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-02
Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-02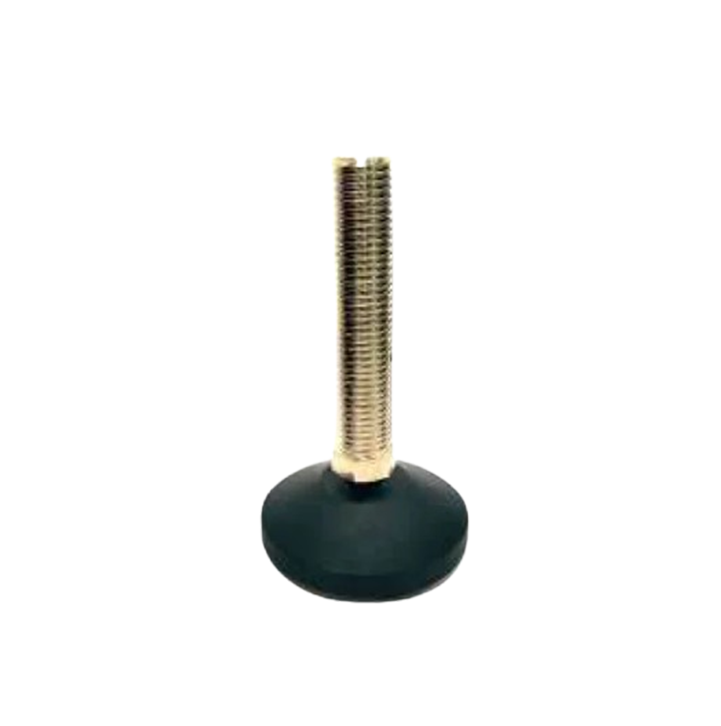 Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-03
Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-03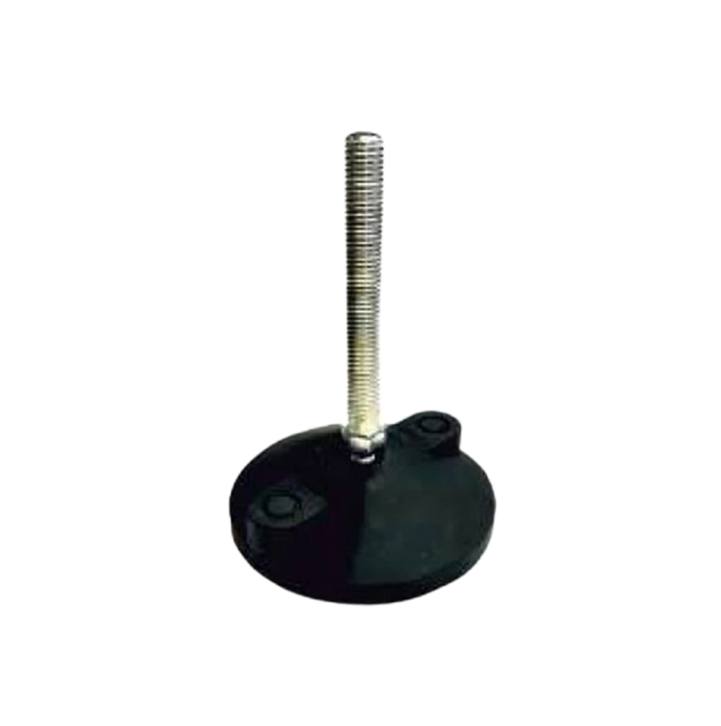 Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-05
Leveling Pad M.S.& S.S. LP-05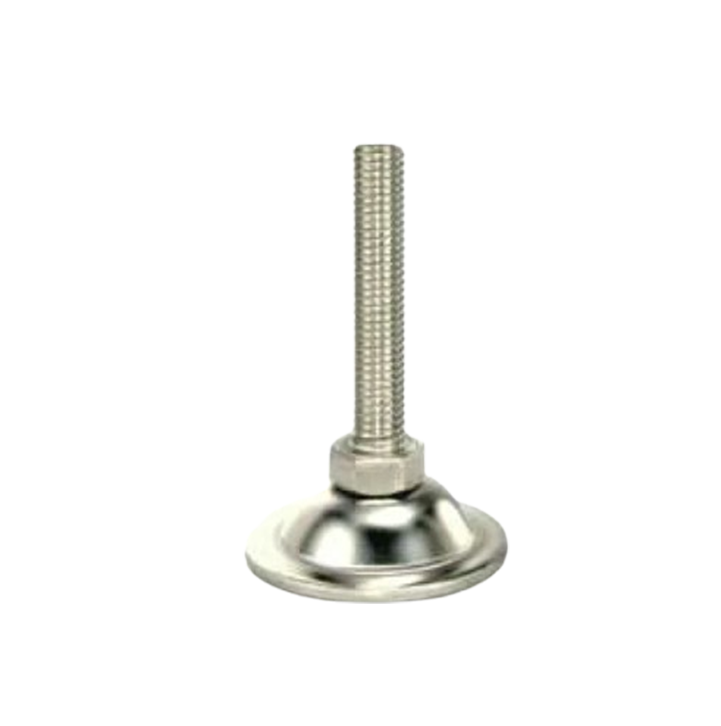 M.S.& S.S. Leveling Pad MLP-01
M.S.& S.S. Leveling Pad MLP-01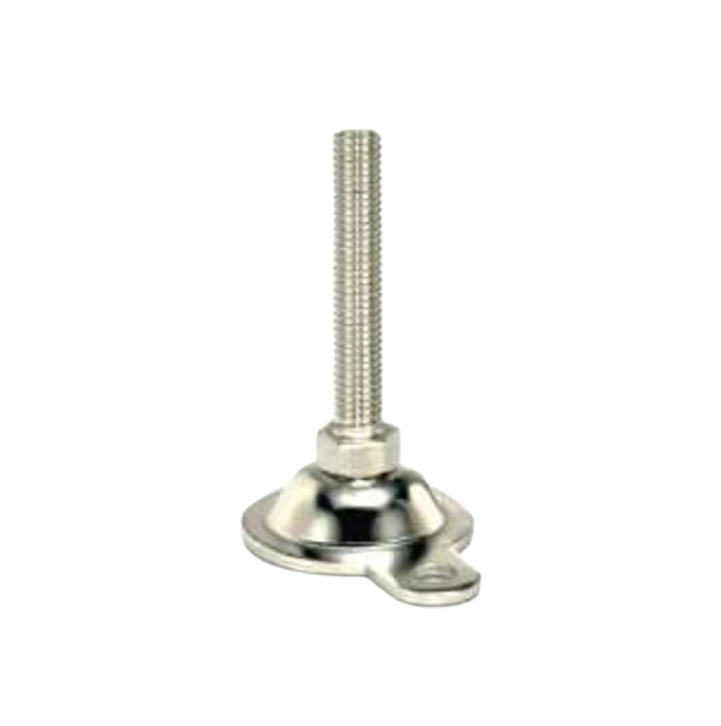 M.S.& S.S. Leveling Pad MLP-02
M.S.& S.S. Leveling Pad MLP-02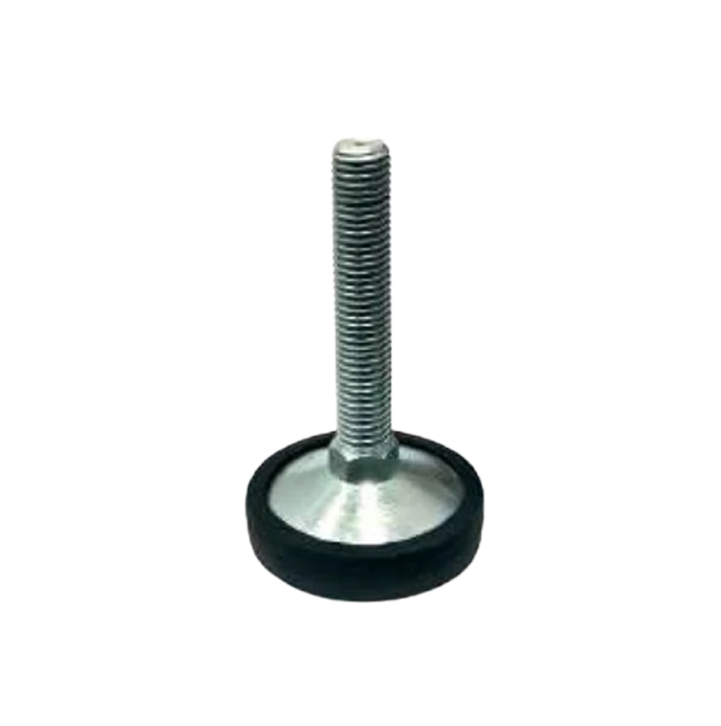 M.S. Leveling Pad MLP-03
M.S. Leveling Pad MLP-03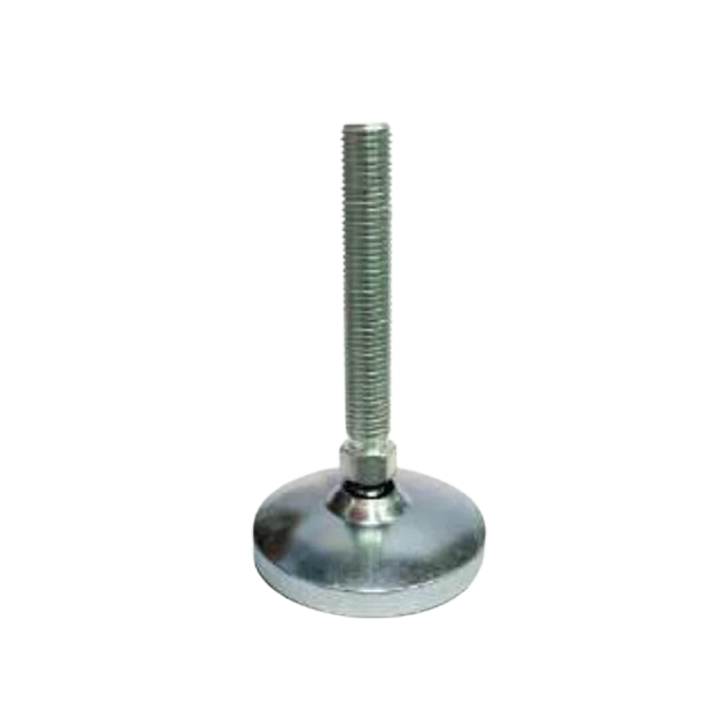 S.S.304 Leveling Pad MLP-04
S.S.304 Leveling Pad MLP-04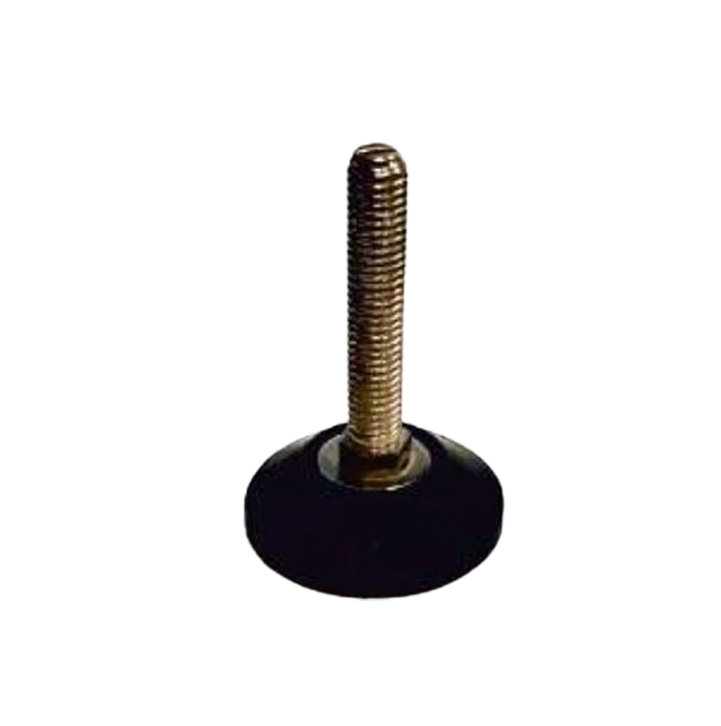 Foot Mount M.S. FM-01
Foot Mount M.S. FM-01 Foot Mount M.S. FM-02
Foot Mount M.S. FM-02 Foot Mount M.S.& S.S. FM-03
Foot Mount M.S.& S.S. FM-03 Clamp 90mm M S S S CL-01-A
Clamp 90mm M S S S CL-01-A Clamp 102mm M S S S CL-01-B
Clamp 102mm M S S S CL-01-B Clamp 54mm M S S S CL-02-A
Clamp 54mm M S S S CL-02-A Clamp 54mm M S S S CL-02-B
Clamp 54mm M S S S CL-02-B Clamp 100mm M S S S CL-03
Clamp 100mm M S S S CL-03 Clamp 100mm M S S S CL-04
Clamp 100mm M S S S CL-04 Clamp 125mm M S CL-05
Clamp 125mm M S CL-05 Clamp M S S S CL-06
Clamp M S S S CL-06 Clamp M S S S CL-07
Clamp M S S S CL-07 Spring Clamp M S S S CL-08-A
Spring Clamp M S S S CL-08-A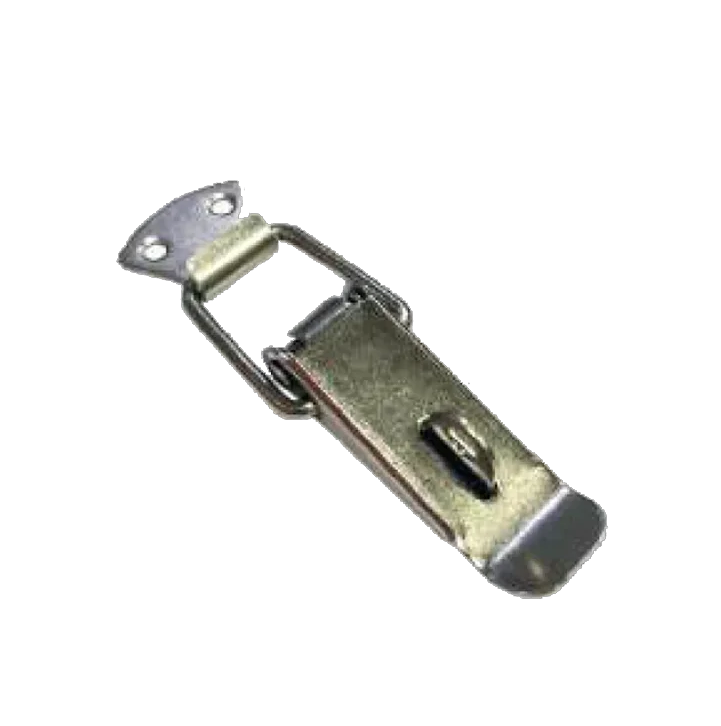 Spring Clamp M S S S CL-08-B
Spring Clamp M S S S CL-08-B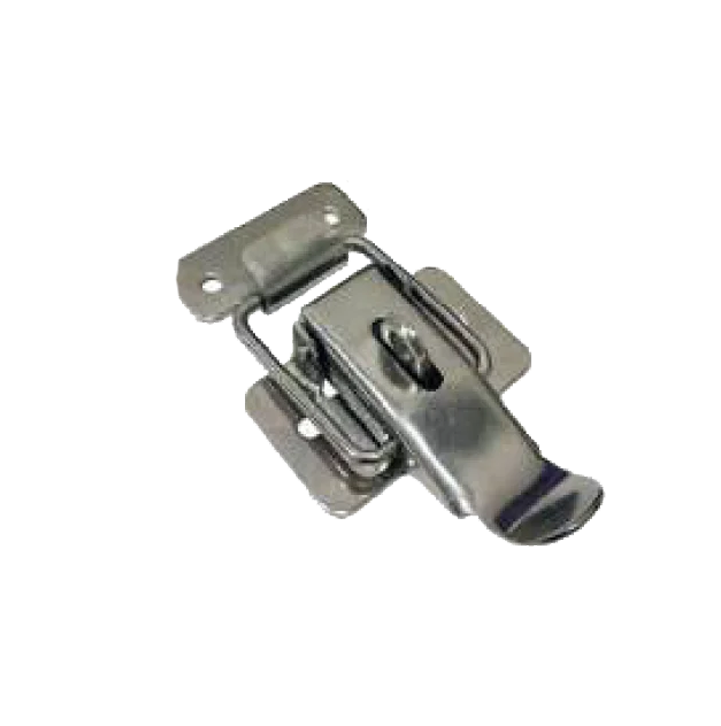 Clamp 110mm M S S S CL-09
Clamp 110mm M S S S CL-09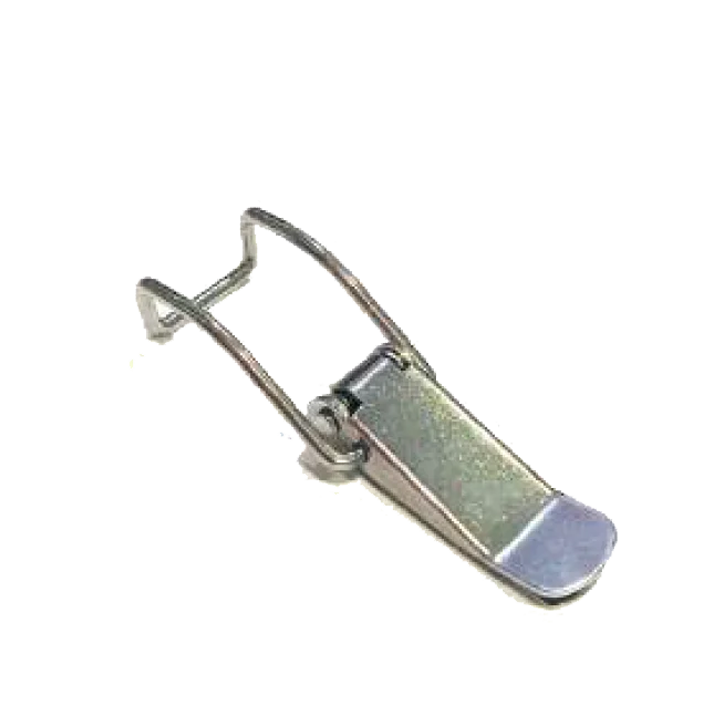 Spring Clamp M S S S CL-11
Spring Clamp M S S S CL-11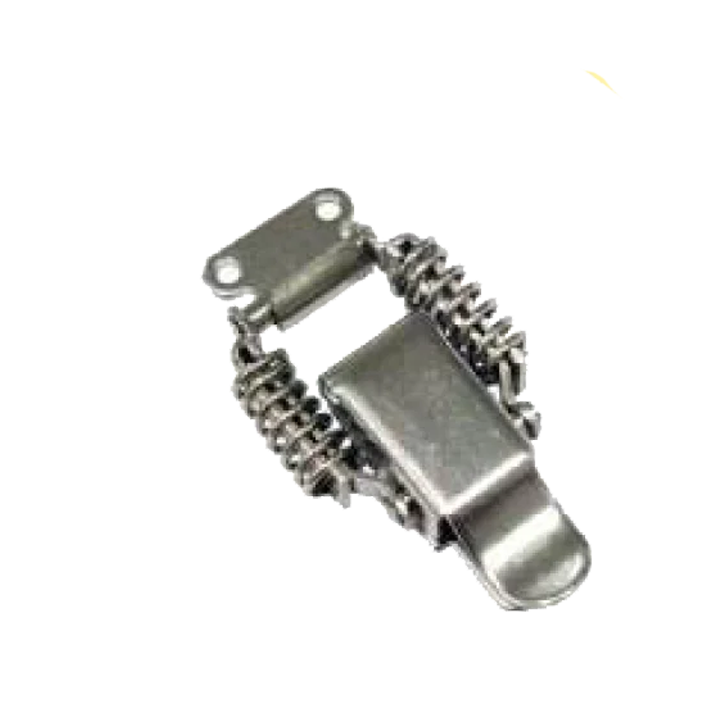 Spring Clamp M S S S CL-12-A
Spring Clamp M S S S CL-12-A Spring Clamp M S S S CL-12-B
Spring Clamp M S S S CL-12-B Small Clamp M S S S CL-13
Small Clamp M S S S CL-13 Die-Cast Lift Off HS-01
Die-Cast Lift Off HS-01 M S Siemens HS-02-A
M S Siemens HS-02-A M S Siemens HS-02-B
M S Siemens HS-02-B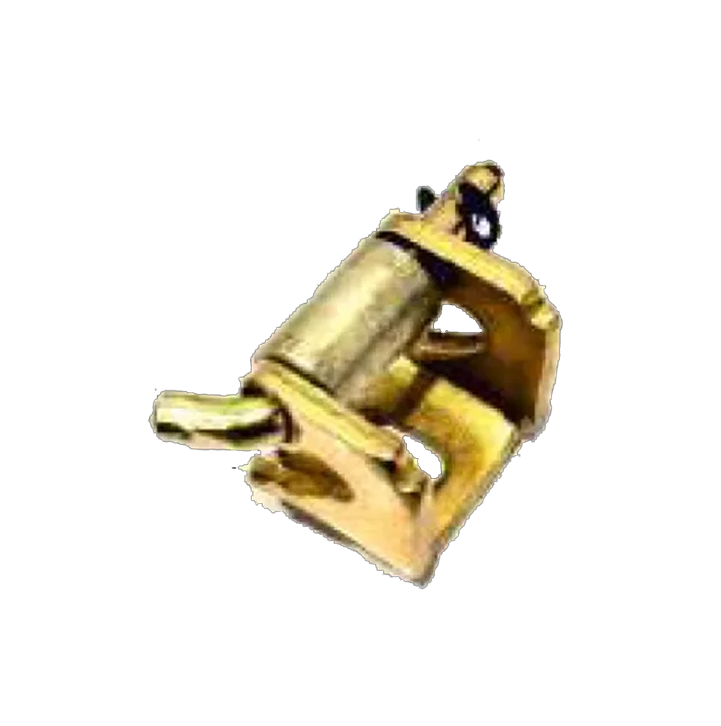 M S Siemens HS-02-C
M S Siemens HS-02-C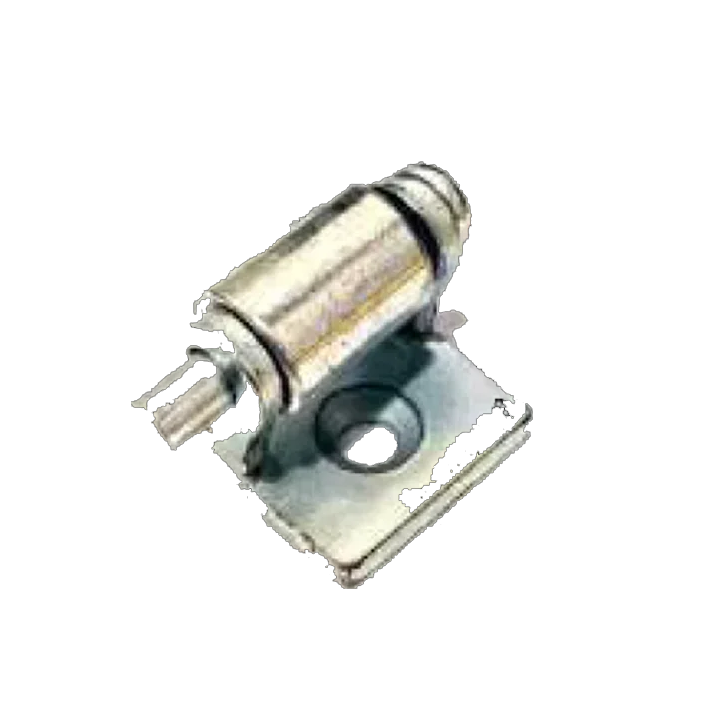 M S Siemens HS-03
M S Siemens HS-03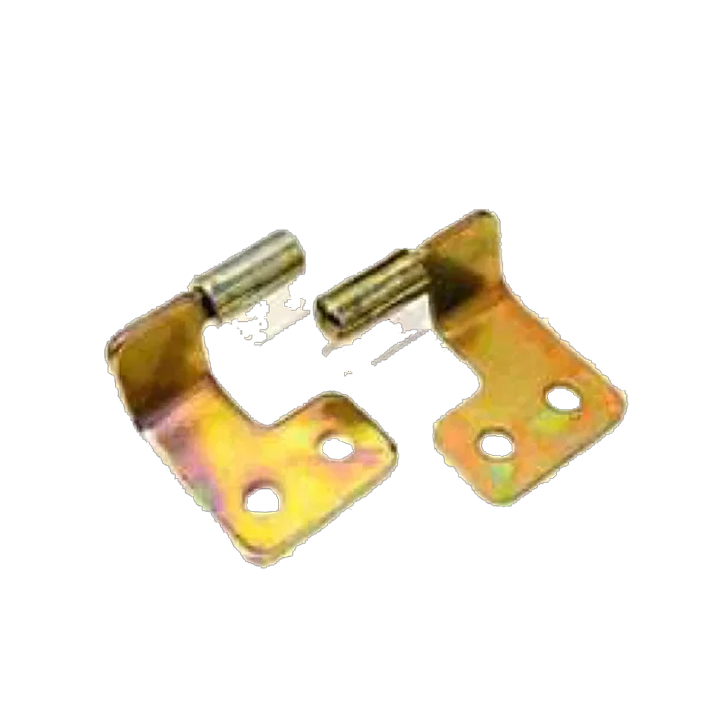 M S Lift Off HS-04
M S Lift Off HS-04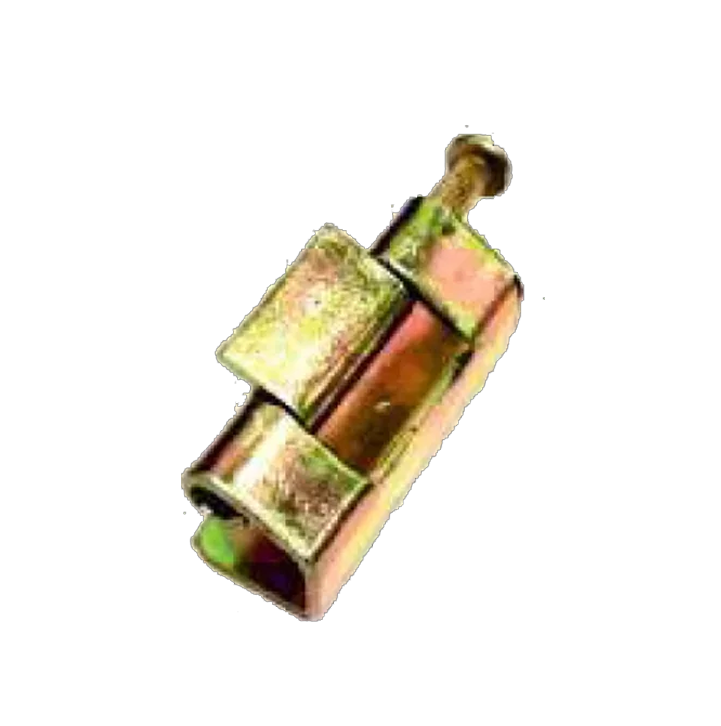 M S Consealed HS-06-A
M S Consealed HS-06-A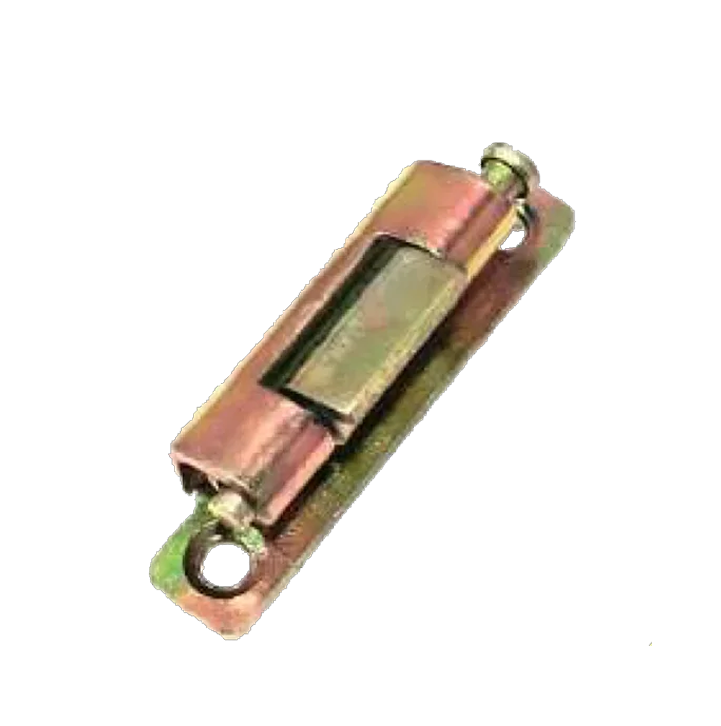 M S Consealed HS-06-B
M S Consealed HS-06-B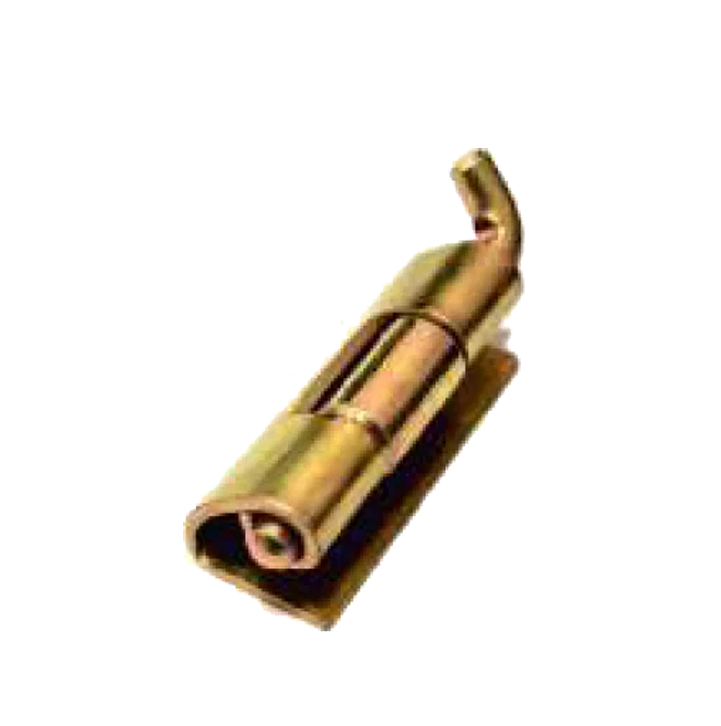 M S S S Consealed HS-07
M S S S Consealed HS-07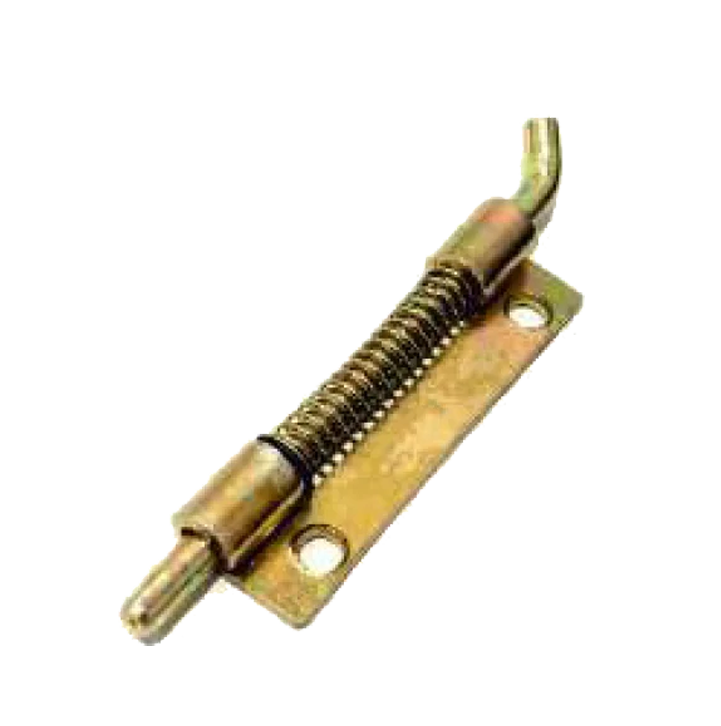 Spring Type S S M S HS-08
Spring Type S S M S HS-08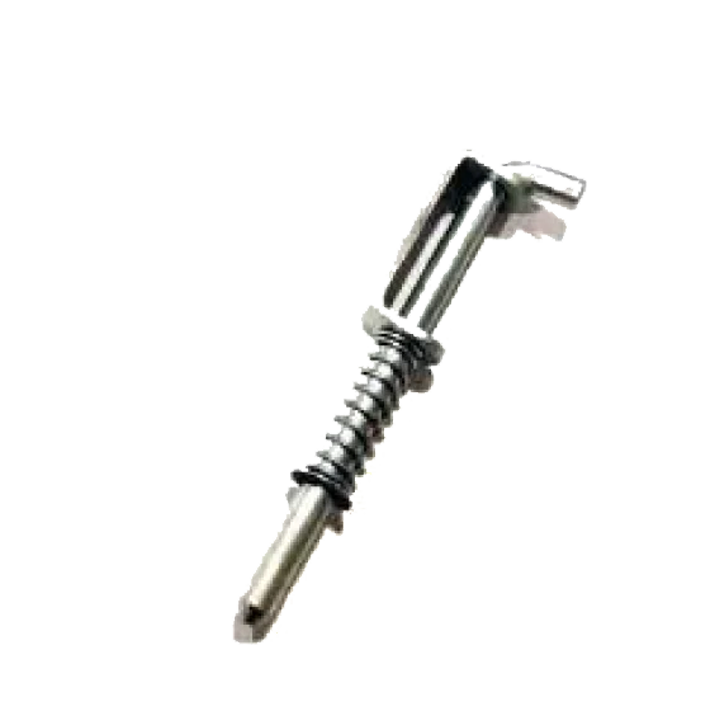 Spring Type HS-09
Spring Type HS-09 L T M S S S HS-10
L T M S S S HS-10 S S Spring HS-11
S S Spring HS-11 Capsule-Type S S M S HS-12
Capsule-Type S S M S HS-12 L T M S S S HS-13
L T M S S S HS-13 Z-TYPE HS-13-Z
Z-TYPE HS-13-Z Poly Profile HS-25
Poly Profile HS-25 Poly 7048/4530 HS-26
Poly 7048/4530 HS-26 Poly 4048/ 2630 HS-50
Poly 4048/ 2630 HS-50 Poly 3048/ 1230 HS-51
Poly 3048/ 1230 HS-51 Poly 5070 HS-27
Poly 5070 HS-27 Poly 4849 HS-28
Poly 4849 HS-28 Die-Cast S.S. 4 Hole HS-30
Die-Cast S.S. 4 Hole HS-30 Die-Cast 50*63
Die-Cast 50*63 Die-Cast 50*76
Die-Cast 50*76 Die-Cast Bolted HS-31-A
Die-Cast Bolted HS-31-A Die-Cast HS-21-B
Die-Cast HS-21-B Die-Cast Rittal HS-32-A
Die-Cast Rittal HS-32-A Mild Steel Rittal HS-32-B
Mild Steel Rittal HS-32-B Polyamide 046 HS-33
Polyamide 046 HS-33 Poly 4 Hole
Poly 4 Hole M.S.& S.S. Hinges HS-38
M.S.& S.S. Hinges HS-38 Die Cast Hinges HS-62
Die Cast Hinges HS-62 M.S. Hinges HS-37
M.S. Hinges HS-37 MS & S.S. Hinges HS-35
MS & S.S. Hinges HS-35 S.S. Lift Off Hinges
S.S. Lift Off Hinges S.S. Butt Hinges HS-40-B
S.S. Butt Hinges HS-40-B M.S.& S.S. Hinges HS-41
M.S.& S.S. Hinges HS-41 Conveyor Guide
Conveyor Guide Conveyor Clamps
Conveyor Clamps Support Base CR-201
Support Base CR-201 Support Base CR-202
Support Base CR-202 Support Base CR-203
Support Base CR-203 Drip Tray Supports CR.252
Drip Tray Supports CR.252 Fixing Washer CR.338
Fixing Washer CR.338 Clamp For Sensor CR.341
Clamp For Sensor CR.341 Connecting Joints CR.501
Connecting Joints CR.501 Support Head CR-502-A
Support Head CR-502-A Support Head CR-502-B
Support Head CR-502-B Side Mounting Bracket CR.513
Side Mounting Bracket CR.513 Round Tube Ends CR.708
Round Tube Ends CR.708 Square Tube Ends CR.710
Square Tube Ends CR.710